As search technologies evolve with the LLM, we all face a new challenge: understanding the difference between SEO (Search Engine Optimisation) and GEO (Generative Engine Optimisation). While both aim to improve online visibility, their approaches and targets differ. SEO focuses on ranking websites in traditional search engines like Google and Bing, while GEO is designed to boost visibility in AI-driven tools that generate answers and summaries from multiple sources. Users rely more and more on AI-powered search engines. The right AI optimization strategy can make the difference between getting noticed or getting left behind in today’s changing digital world.
Key Statistics About This Topic
-
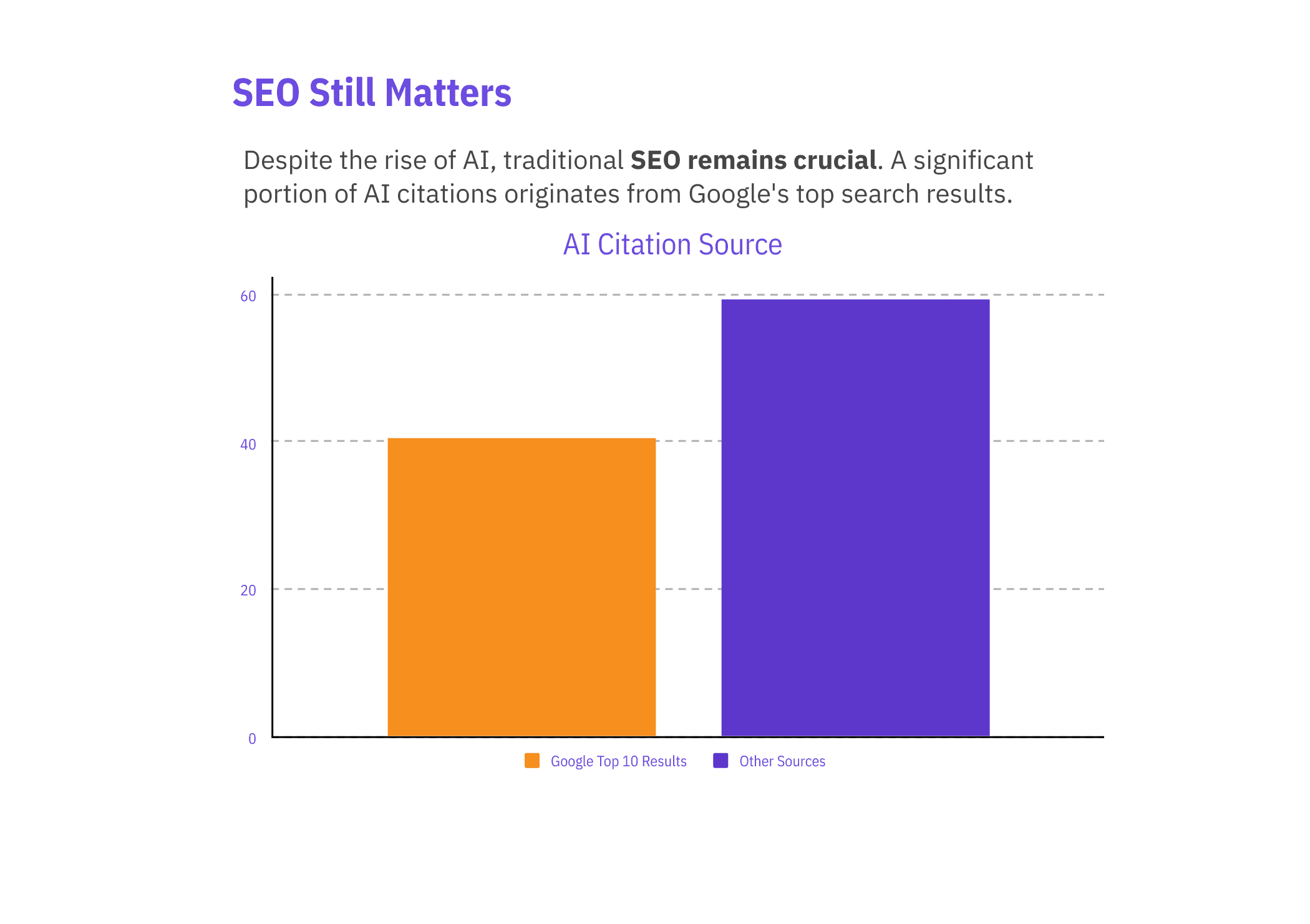
40.58% of AI citations originate from Google’s Top 10 search results – showing that strong SEO rankings remain crucial for visibility in generative search.
-
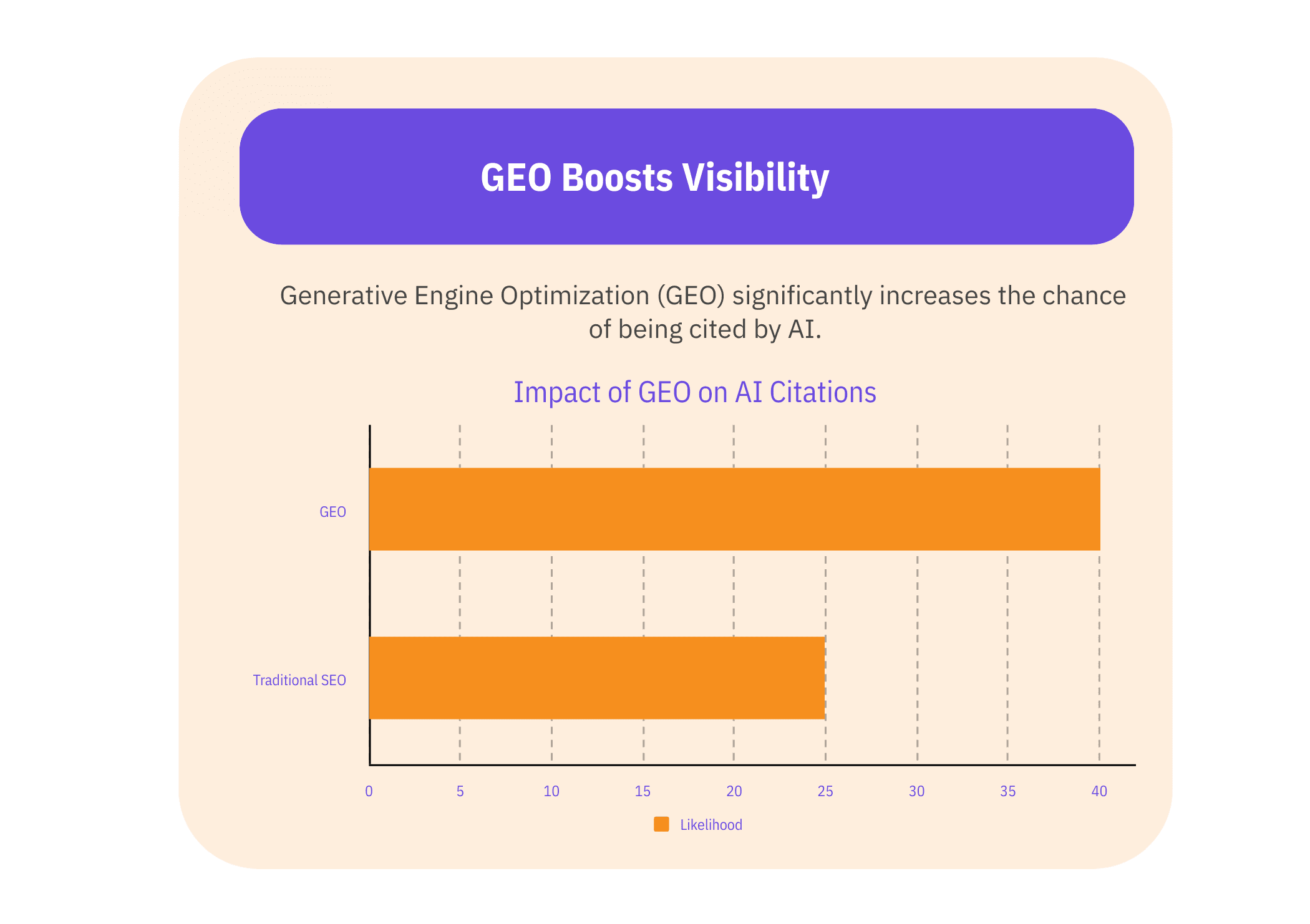
GEO can increase the chance of being cited in AI-generated answers by up to 40% – proving the value of optimizing content specifically for AI engines.
-
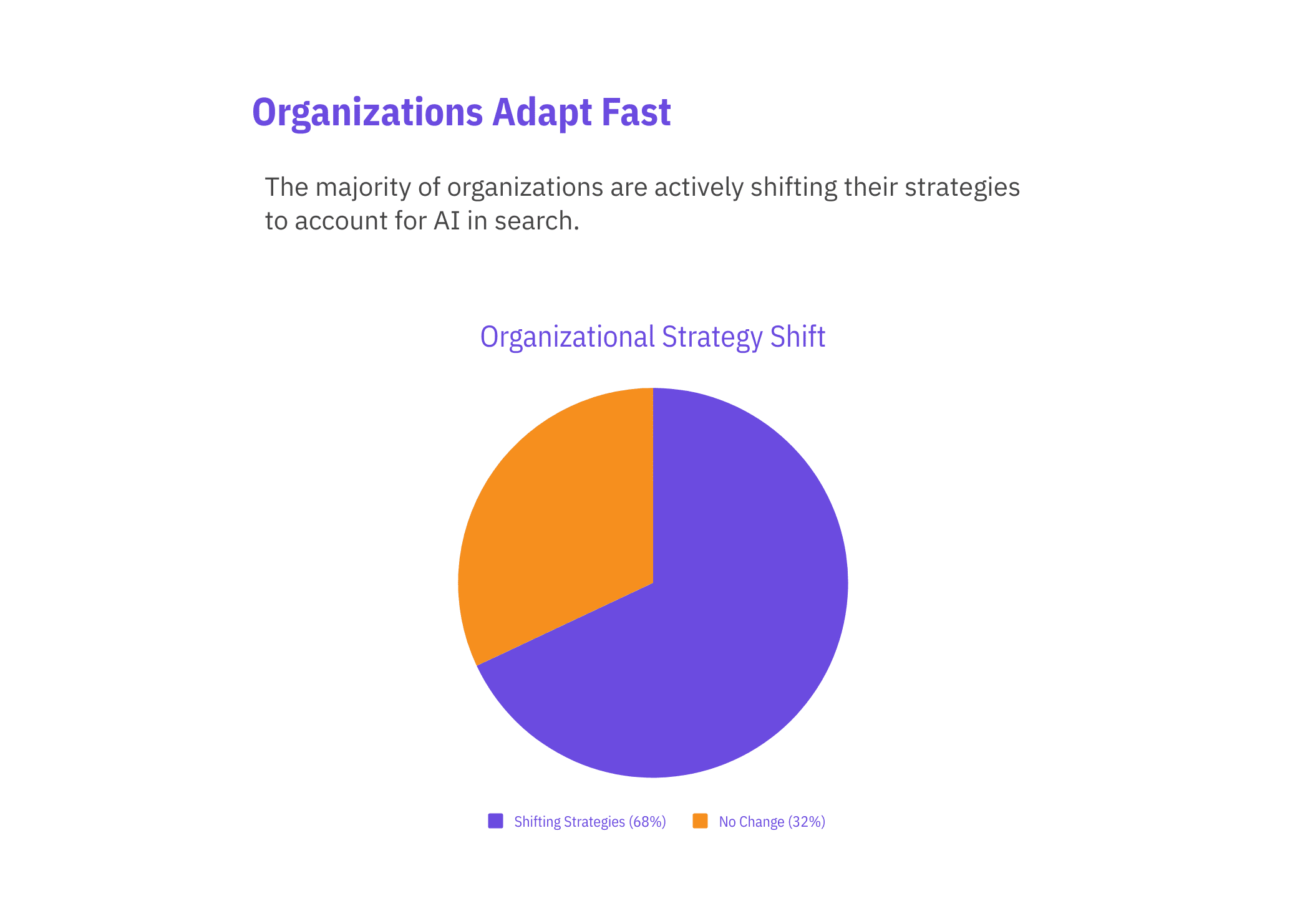
68% of organizations shift strategies for AI search – blending traditional SEO with AI-focused tactics to maintain brand visibility.
Key Takeaways from this article
- SEO targets traditional search rankings; GEO optimizes for AI-generated responses.
- Each approach requires different strategies and key metrics for measuring success.
- Understanding both methods helps websites stay visible as search trends shift.
Fundamentals of GEO and SEO
GEO vs SEO
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) and Search Engine Optimization (SEO) are both important for online visibility, but they focus on different types of search platforms and use unique approaches. Understanding the main ideas and methods behind each one helps digital marketers decide how to stay visible as new technologies emerge.
What Is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is a process of improving a website’s visibility in AI-powered search platforms. These include tools like ChatGPT, Google SGE, Microsoft Copilot, Perplexity AI, and other engines using Large Language Models.
GEO aims for content to be easy for artificial intelligence systems to read, understand, summarize, and include in their answers. AI search tools do not simply give a list of links. They generate single, detailed summaries or responses based on many sources at once. That means structured, high-quality, and relevant content stands out.
Key elements of GEO include:
-
- Using clear headings and organized sections
-
- Adding structured data like schema markup
-
- Giving direct answers to common questions
-
- Citing accurate sources and keeping information up-to-date
Since AI summarizes information, GEO can increase content visibility even if fewer users visit directly. Being mentioned or cited in an AI-generated answer helps keep brands present in new search formats.
What Is Search Engine Optimization (SEO)?
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the long-established strategy used to help websites appear at the top of traditional search engine result pages (SERPs). Platforms include Google, Bing, and Yahoo, which still present lists of website links related to search queries.
SEO involves several main practices:
-
- Researching and using target keywords
-
- Building high-quality backlinks to improve authority
-
- Writing valuable and original content
-
- Optimizing metadata, titles, and descriptions
Traditional SEO works by making web pages easier for search engines to understand and index. Websites with strong SEO tend to get higher rankings, which often leads to more clicks and traffic from users browsing search results.
SEO relies heavily on keywords and link-building, but also takes into account user experience, mobile-friendliness, and site speed. Though AI influences search engines more every year, these core techniques remain vital in digital marketing.
Core Differences Between GEO and SEO
GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) and SEO (Search Engine Optimization) focus on different aspects of search discovery. While SEO is built around traditional search engines and their ranking systems, GEO shifts towards AI-driven platforms where context, conversation, and content quality matter more.
Target Platforms and Search Engines
SEO is aimed at traditional search engines like Google, Bing, and other well-established platforms. These engines rely on crawlers to index website content, displaying a list of links called search engine results pages (SERPs).
GEO, on the other hand, is designed for AI-powered search engines. These include ChatGPT, Microsoft Copilot, Perplexity, Gemini, and similar tools. Instead of standard result pages, these platforms generate direct, summarized, and context-aware responses.
The main difference is in audience reach and platform priorities. SEO strategies help websites stand out in classic link-based searches, while GEO adapts content to algorithms that power AI-driven search, making information easier for engines to read, interpret, and cite in results.
Difference in Ranking Factors
Traditional SEO ranking depends mostly on keywords, metadata, backlinks, and technical site quality. Algorithms assess how well content matches search intent, its popularity (measured by links), and site reliability.
GEO uses different standards. AI-driven search engines focus on the clarity, relevance, and structure of content for extracting quick answers. Content needs to address questions directly, use conversational language, and include sources that AI models can easily recognize and cite.
A summary of key ranking factors:
| Factor | SEO (Google, Bing) | GEO (ChatGPT, Copilot) |
|---|---|---|
| Keywords | Important | Moderate |
| Content Structure | Important | Very Important |
| Backlinks | Very Important | Less Important |
| Source Citations | Moderate | Very Important |
| Conversational Tone | Optional | Required |
User Interaction and Experience
With SEO, users interact mainly with SERPs. They browse through multiple links, select a website, and then look for information themselves. The experience is built around user choice and website engagement.
For GEO, the interaction shifts to querying AI search engines like ChatGPT or Copilot. Instead of sifting through many options, users receive a single, summarized answer. This result is generated after AI analyzes and synthesizes information from several sources.
This new style changes how people explore content online. There are fewer clicks to individual web pages and a greater focus on quick, accurate responses. As a result, getting cited or featured by AI engines becomes more important than just ranking high on traditional SERPs.
Optimization Strategies for GEO
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) requires adapting traditional SEO approaches to fit AI-driven search engines and Large Language Models. Effective GEO relies on structured content, clear signals for AI summarization, and maintaining strong credibility through content quality and authority.
Optimizing for AI Summarization and Attribution
AI search engines like ChatGPT and Microsoft Copilot pull information from many sources to summarize answers for users. To improve GEO, content should be concise, direct, and answer common questions clearly.
Best practices include:
-
- Use short paragraphs and bullet points for clarity.
-
- Place answers near the top and avoid burying key info.
-
- Provide context for each answer so AI can use it independently.
AI models are more likely to cite and attribute sources that offer clear and direct responses. This means websites should include original insights or data and reference trustworthy external sources when applicable. Cited claims and referenced URLs increase the chance an AI engine credits the content as the source.
Structured Data and Schema Markup in GEO
Structured data and schema markup help AI engines understand and categorize information from websites. This is essential for GEO because AI models use these signals to identify specific answers, entities, and relationships.
Key steps:
-
- Add schema markup for FAQs, products, reviews, and organization details.
-
- Mark up lists, how-tos, or recipes so AI can extract step-by-step content.
-
- Use consistent headings and table formats for structured answers.
Properly structured content increases the chance of being selected for featured snippets or AI summaries. It also helps ensure that brand names, products, and important context are cited correctly by generative models.
E-E-A-T and Content Quality for Generative Engines
E-E-A-T stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. For AI-driven search engines, these principles are critical to how Large Language Models decide which content to include and cite.
Writers should showcase experience by adding author bios, credentials, or first-hand examples. Authoritativeness is boosted by linking out to reputable sources and gaining backlinks from industry leaders.
To build trustworthiness, keep content up to date, accurate, and transparent about sources. Avoid clickbait or unsubstantiated claims. Use clear language and address user intent directly. AI models prefer well-researched, unbiased content that aligns with structured data and transparent attribution, making E-E-A-T a core part of any GEO strategy.
GEO Metrics and Emerging KPIs
GEO measures performance by how often AI-powered systems reference, quote, or summarize a website’s content. Key generative metrics include:
-
- AI Citation Frequency: Counts how often an AI tool (like Google’s AI Overviews or ChatGPT) cites a website or author.
-
- Citation Prominence: Measures how visibly content is featured in AI-generated answers.
-
- AI Referral Traffic: Tracks visitors arriving through links or mentions in AI summaries.
-
- Contextual Accuracy: Ensures references are correct and match the intended topic.
GEO does not focus on traditional search rankings. Instead, it tracks inclusion and correct representation in AI-generated summaries. Businesses might also monitor brand mentions or references within synthesized responses. These metrics help measure credibility and influence within new AI-driven search environments.
SEO Metrics: Traditional Approaches
SEO performance is often matched to how well a website ranks for specific keywords in search engines like Google and Bing. Important metrics include:
-
- Search Rankings: Where pages show up for targeted terms.
-
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): The percentage of users who click on a search result.
-
- Bounce Rate: The rate at which visitors leave a page without interaction.
-
- Time on Page: How long visitors stay on a specific webpage.
-
- Conversions and Conversion Rate: How many users complete a goal (like a purchase or sign-up), divided by the total visitors.
SEO metrics aim to show how discoverable and engaging content is in traditional search results. High rankings and good user behavior signals often lead to more organic traffic and better conversion rates.
Comparing Impact: Click-Through Versus Citations
GEO and SEO affect visibility in different ways. SEO drives website traffic through high rankings, leading to clicks and direct visits. Here, success is tracked using CTR, search positions, and onsite behavior like time on page or bounce rate.
GEO may increase brand exposure even if users never click through, as content can be quoted in AI-generated responses. Citations and mentions can grow authority and reputation, but do not always bring direct visits or conversions.
SEO metrics tend to focus on actions taken on the site, while GEO metrics focus on how often content influences AI-generated results. Both sets of metrics offer different but complementary views of digital performance.
Future Trends and the Evolving Search Landscape
AI-powered search engines, such as Google’s Gemini and Microsoft’s Copilot, are becoming central to how users ask questions and get information. These platforms use natural language processing to understand complex user queries and offer answers in a conversational style. More searches also now involve voice assistants like Siri and Alexa. Voice search changes how queries are framed, with users speaking in full questions rather than short phrases. As a result, content optimized for voice and conversational search is gaining attention.
Generative AI can deliver multimodal results, mixing text, visuals, and sometimes video or audio. This shift makes it necessary for websites to diversify their content formats. Businesses must adapt to these new AI-driven channels to stay relevant and reach users wherever they search.
Key Opportunities:
-
- Early Adoption: Adopting GEO strategies on new platforms can help brands stand out quickly.
-
- Broader Reach: AI-driven results appear on different devices, including voice assistants, smart speakers, and mobile apps, broadening the audience.
-
- Content Variety: Digital marketers should experiment with new formats such as infographics, podcasts, and short videos to meet the content needs of evolving platforms.
Keeping up with shifts in user queries and platform requirements allows brands to improve their online visibility and digital presence.
Blending GEO and SEO in Digital Marketing Strategies
SEO and GEO work best together. SEO provides a solid foundation for organic search rankings, while GEO focuses on tuning content for generative AI responses and conversational modes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the fundamental differences between Generative Engine Optimization and traditional Search Engine Optimization?
GEO aims to make content easy for AI systems to interpret, summarize, and reference in AI-generated answers. This requires structured data, clear attributions, and verified information. While SEO boosts site visits, GEO focuses on content visibility within AI responses.
How can Generative Engine Optimization impact content creation processes differently than SEO?
Unlike SEO, which often targets keyword placement and natural language, GEO demands precise formatting and easy-to-read data. Writers must anticipate how AI engines might select and display their content in answers.