About Koray Tuğberk GÜBÜR
Koray Tuğberk GÜBÜR is an internationally recognized SEO strategist and the founder of Holistic SEO & Digital. Over the last decade, Koray has shaped the way global brands approach online visibility, pioneering techniques in Semantic SEO and topical authority and publishing hundreds of SEO experiments that decode how search engines perceive relevance, authority, and user behavior. His portfolio stretches from the competitive casino sector to international e-commerce, B2B, and retail companies. Beyond consultancy, Koray is a prolific educator his “baby search engine” projects and detailed case studies consistently clarify some of SEO’s most challenging concepts for professionals worldwide.
Interview- How to Structure Content, Clusters and Internal Links to Dominate the Entire Subject
In the world of SEO, few names command as much respect and curiosity as Koray Tuğberk GÜBÜR. His research has not just added to the industry’s collective knowledge but has challenged long-standing assumptions, giving brands the tools to compete in high-stakes niches. The casino industry, with its brutal competition and constantly shifting regulatory landscape, provides the perfect testing ground for strategies around topical authority. Koray’s SEO work bridges theory and practice, showing how SEO testing can uncover the hidden mechanics of Google’s algorithms. In this conversation, he explores topical authority through the unique lens of the casino industry, one of the most competitive and complex verticals in SEO.
Q: The casino niche is one of the most competitive in SEO. From your perspective, Koray, what makes topical authority especially critical in this industry?
A: Until the 1st August 2018, we were able to manipulate Google’s query behaviors, statistics, and data very easily. We were using macros (user behavior scenarios we automate with multiple laptops to blur search engine’s decision trees), virtual machines (to prevent search engines from catching our fingerprints), and different types of VPNs (to imitate multiple users with multiple IDs) to hide our fingerprints and blend the fake search activities with the real ones that we were supporting through pop-up types of traffic sources. We were able to manipulate auto-completions, and we were even able to affect Google’s “Did you mean this’ behaviors. This was a good method to rank sources easily, because it was giving the signal of “popularity”.
Google always favors popularity as a brand, as an entity type (which entity-type is searched more), entity (which entity is searched more), or the “click-selection” (which source is selected more). But, after the Medic Update, we lost all of our PBNs, and we restarted from zero to be able to fix everything one more time. Topical Authority was an idea that came from a need. Because we were not able to manipulate “popularity” anymore, and Google was using something called “RankMerge”, meaning merging links’ PageRank value with the “traffic”. Because, we were manipulating links, in the link graph for taking the attention of search engines as an authority, but also we were manipulating the traffic/popularity. Google wanted to see “websites that everybody visits, but nobody links, such as porn sites, and websites that “everybody links but nobody visits” such as academic websites’ true value. RankMerge was a new lens for the blind librarian, and we couldn’t manipulate it after they improved their fake traffic detection algorithms.
When we talk about topical authority, we are referring to how cost-efficient a source is to crawl, index, evaluate, rank, and continuously test, as well as how accurate, unique, relevant, and responsive its information remains across a topic. If a source provides the highest level of coverage for closely related queries while maintaining the lowest possible computational cost for the search engine, it becomes the most efficient option to satisfy users’ needs behind those queries.
In the casino industry, the CTR, also referred to as the click-selection rate, is as important as link-graph centrality. However, most of these elements are external to the search engine’s core systems, which makes them easier to fake or manipulate and therefore more volatile in the decision-making process. In contrast, factors such as topicality, topical coverage, accuracy, relevance, and responsiveness are internal signals that require time, consistency, and depth to establish. Because Google is a complex adaptive system, it prioritizes signals that are harder to manipulate and that contribute to long-term search engine trust. In our Fundamentals of Search Engine Optimization keynote, we demonstrate how all ranking factors and signals can be grouped into six major categories under the Holistic SEO framework. Within this structure, external factors fall under NavBoost, while internal factors are aligned with Topical Authority.
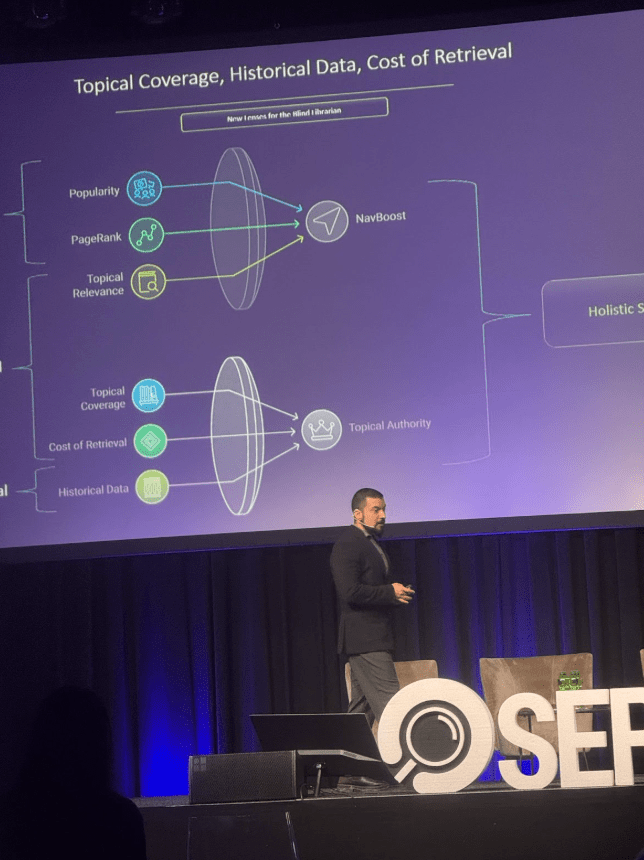
Topical Authority is the most permanent and determinant factor, regardless of the industry or vertical differences. It is the best complementary factor for search engines’ trust signals, as the design of the Anand Shukla, one of the creators of Google’s AI Mode requires it everywhere.

Or, as Chief of Ranking in Google, Pandu Nayak states a similar statement during the anti-competition lawsuit as a witness.

He clearly states that Google reduces the cost of retrieval by avoiding expensive algorithms for every website, instead triggering NavBoost and topicality checks to determine whether a site is worth deeper processing. There are hundreds of additional proofs we could reference from the “contentEffort” perspective using the Google leaks, but for the scope of this discussion, this summary is sufficient.
Q: You’ve published hundreds of SEO experiments. Based on your findings, which signals matter most for establishing topical authority in high-stakes niches like gambling?
A: We have published more than 500,000 words of case studies across 180+ websites, openly sharing their brand names. As a community, we have also published over 390 public results in the last two years. Across all of these cases, the same recurring patterns consistently prove our concepts, methods, and practices.
The first and most critical pattern is branded search demand. Without branded search demand, a website is expandable to the search engine, because there is no proof of identity, loyalty, or user-driven authority.
The second pattern relates to technical efficiency. A website should respond in under 100 ms for crawling systems, maintain 99% HTML crawl hits on canonical URLs, and return 99% 200/304 status codes. This tells the search engine:
“I do not waste your time, bandwidth, or computational cost.”
When these conditions are met, even weak technical areas can be balanced by strong content signals.
The third pattern is popularity and long-term trust signals. Search engines test and rank a source through initial ranking and re-ranking.
- Initial ranking is a temporary test to measure early reactions.
- Re-ranking is a deeper test, based on historical data, to evaluate whether the source deserves higher ranking scales.
Re-ranking is tied to ranking states and thresholds. Once a website enters a positive ranking state by exceeding quality thresholds, it will continue to rise, even if the site makes short-term mistakes in content, layout, or technical structure. The momentum protects the rankings until the state changes.
This is one of the core purposes of Topical Authority: to push a website into a positive ranking state, then expand that momentum. Sometimes we achieve this by creating a perfect subfolder, allowing that subfolder to gain rankings even while the main domain struggles. Once the subfolder proves itself, we reflect its character across other sections, forcing the search engine to evaluate the site based on its best-performing area, not its historical weaknesses.
In other cases especially for new projects we prioritize impressions over clicks. When a website reaches 10,000+ daily impressions, re-ranking begins, and positive ranking states appear. Until the site fulfills its potential within that state, it will not drop or neutralize. That is when we scale topical coverage rapidly, because momentum (speed of publishing and updating) multiplies impact.
- Momentum = publishing and updating faster
- Coverage = covering more entities, activities, and attributes
- Depth = sharper, more complete topical layers for each entity
To illustrate:
A website that publishes 10,000 documents in one month and covers 10,000 entities within a topic such as bonuses, demo accounts, payment methods, withdrawal conditions, tips, and rules will gain far greater momentum, clarity, and topical coverage than a website that publishes 500 overlapping documents in six months. The first source has a much higher probability of success.
However, after 2021, we began to observe that websites publishing too aggressively without control triggered manual penalties. I explained these examples in detail in my Saigon 2023 keynote, and again in our Chiang Mai SEO session, both of which are included in the Topical Authority Course. The concept is the same from both stages:
Momentum works but only when controlled, layered, and contextually consistent.
- The concept of momentum exposes the limits of human content production, which is why Google references “total human effort” in the Quality Rater Guidelines and uses “contentEffort” as a measurable signal in the Content Warehouse API leak. If a website publishes one million documents in a single day, it is, by definition, fully automated, and that triggers deeper scrutiny. After the rise of ChatGPT, Google responded by striking content deals with Reddit and commercially amplifying forum data boosting Reddit’s traffic and stock value in the process. This shift confirms that Google’s systems now heavily prioritize perspectives, lived experience, and personalized language. For this reason, to achieve higher language scores and trust signals, we intentionally diversify our tones and narrative styles across the content network.


We can highlight countless websites as examples, but the pattern is simple: while presenting factual, objective language, we also integrate Q&A sections, polls, and opinion modules supported by structured data to demonstrate real human involvement. The same applies to slot games, football betting, and other niches. By embedding question-answer pairs, user perspectives, and expert references tied to real entities from Google’s Knowledge Graph, we increase perceived human effort, strengthen topical depth, and amplify the trust signals Google rewards.

This is why the page that initially lost visibility during the early Helpful Content Update regained its rankings significantly after we launched a comprehensive topical map and a semantic content network.

Q: How does building authority in the casino space differ from doing so in less competitive industries like SaaS, eCommerce, or local SEO?
A: Theoretically, there is no difference. Practically, everything scales in bulk. As explained in our SEO Case Study on quality thresholds (https://www.oncrawl.com/technical-seo/importance-quality-thresholds-predictive-ranking/), every topic, industry, and vertical operates under different algorithms and quality requirements. Index size, average PageRank, and the volume of historical data vary across industries, which is why the same ranking patterns can appear faster in some niches and slower in others.
The casino industry is unique because it contains the highest concentration of expired-domain abuse, reputation abuse, hacked sites, negative SEO attacks, PBN activity, and CTR manipulation. When 40+ expired domains and hundreds of DMCA complaints target the same brand every week combined with artificial traffic manipulation it forces search engines into a cautious and sometimes confused state. In these scenarios, it can be more effective to target generic casino terms instead of brand names directly.
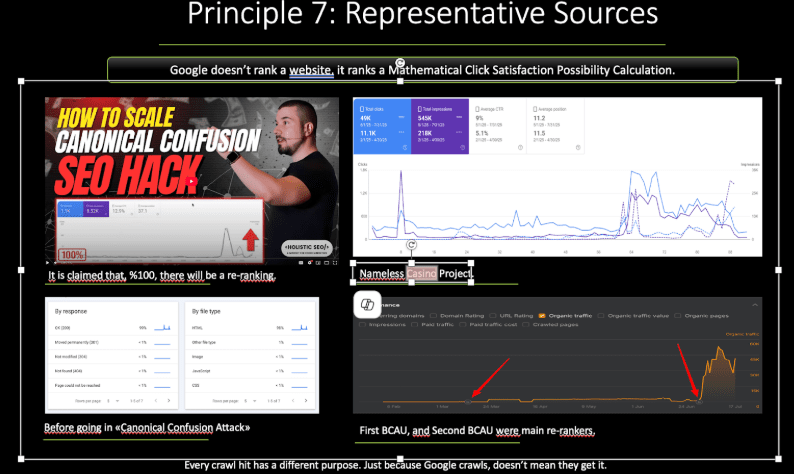
This chaotic behavior is common in non-regulated regions such as Southeast Asia, Latin America, Turkey, and parts of Africa. In regulated markets, however, the SEO landscape is more stable and follows clearer principles. Yet in both environments, the constants remain the same: Topical Authority and the core fundamentals of Information Retrieval. For instance, during our SERPConf 2025 keynote, we demonstrated a canonical confusion attack to show how these principles apply even in hostile SERP conditions.
The video is below:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qWLhHwX4HMs
In that video, we explained that another core update would arrive and that a re-ranking phase would follow. Even the thumbnail signalled this, with the arrow pointing forward. And it happened exactly as predicted. We won two core algorithm updates, one in March 2025 and another in June 2025.
During this period, we saw major growth in the SEA region, outperforming competitors using DMCA abuse, PBN networks, hacked domains, and expired-domain schemes. We achieved this by combining Topical Authority with classic black-hat techniques. This proves an important point: it is not “white-hat vs. black-hat.” It is both which is the essence of Holistic SEO: whatever works, applied in a controlled system.
We used the same core-update-focused strategy for this casino project as well. The methodology is explained in detail here:
So whether the niche is casino or not, our approach does not change. Only the combination of methods, thresholds of ranking, and required budget change. Holistic SEO is not about excluding one method in favor of another it is about using every valid tool, technique, and signal available to win rankings.
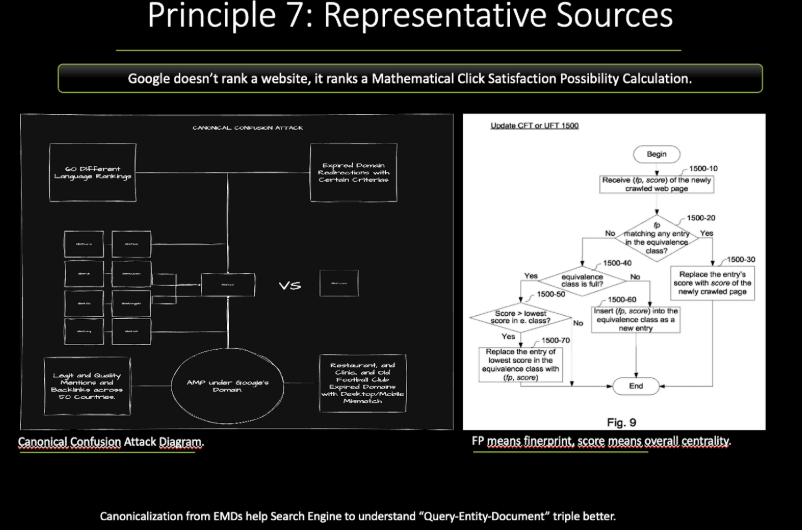
In terms of the canonical confusion attack, what we have performed is explained in the slide below.
And, you can see that our technical KPIs are also in place.
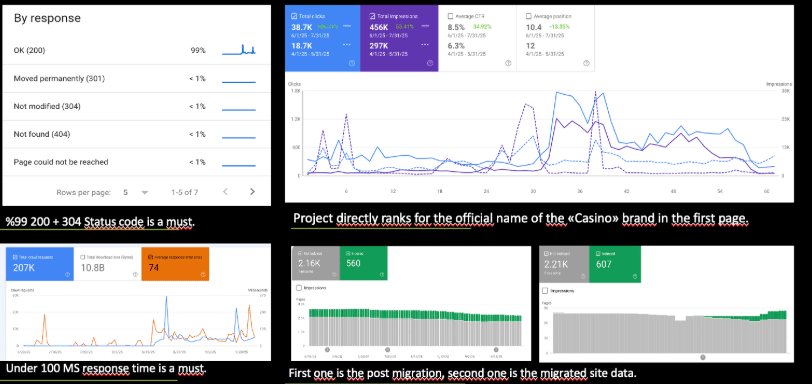
Currently, we are performing migration from one domain to another, while changing the source from brand-term rankings to the generic term rankings, to avoid DMCAs, and having a more historical data rich domain network. Because, casino-related SEO business also means domain business. If you have a stronger domain network, you have advantage of a PageRank, and trust-signal rich domain redirection chain that creates velocity, and freshness while giving you always a new chance to rank, and exceed thresholds. The important thing is to know which domains work, and which ones don’t.
Q: Many casino sites produce endless bonus pages and game reviews. What common mistakes do you see in how affiliates and operators structure content, and how can they improve clustering and internal linking?
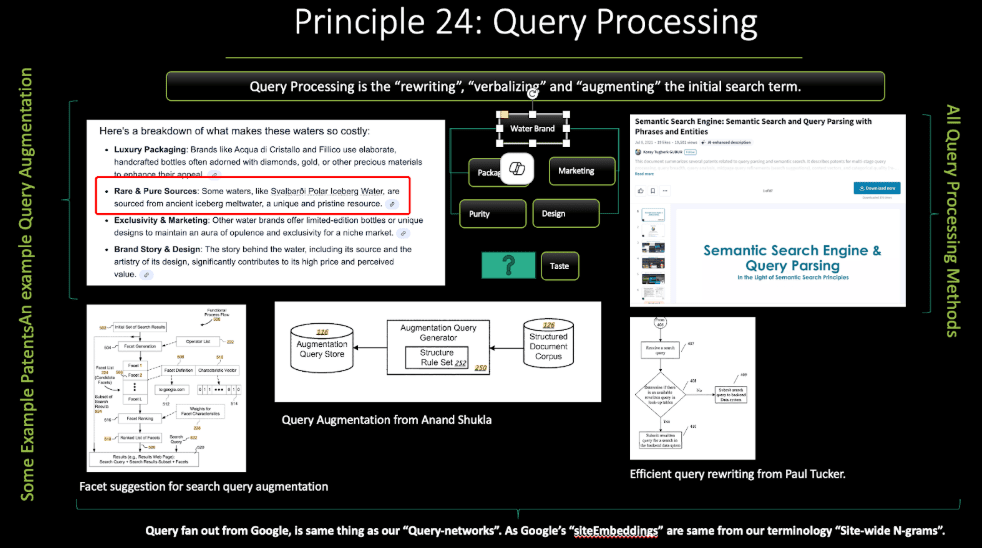
A: “Opening a new page” means decreasing the “Ranking signal per web page”, and “PageRank” mainly. Thus, in many of our lectures in the topical authority course, we explained when to open a new page. We created a term called, “QDP – Query Deserves Page”, and “PSQ – Page Serves Query”. To understand when to open a new page, and merge multiple entities under the same context, you should understand the criteria below.
Query has high search demand, query has different entities, query has low similarity, query has a pattern. If 3 out of 4 criterias here are valid, feel free to open a new page, and contribute to the index-size, with a similar vocabulary of the similar URLs. The main problem here is that thinking that casino-related “Page opening criteria” would be different than the “e-commerce”, but in reality, it is not. Search engines have similar machine-learning algorithms that rely on fundamentals of information retrieval. The system below is demonstrated in our Cyprus speech, during the I-conn, along with some other casino projects. And, this is one of the projects that we have triggered a re-ranking, by creating a new subfolder, and making it high-quality, while using that sub-folder to trigger a re-evaluation for the entire website. The slide below demonstrates for which Holster we should open a new page, or not. If it has a yellow border, it means it needs to be a new page. And, in some cases, we don’t open a new page, or we merge 3 entities under the same page, due to the “term-weight calculation”.
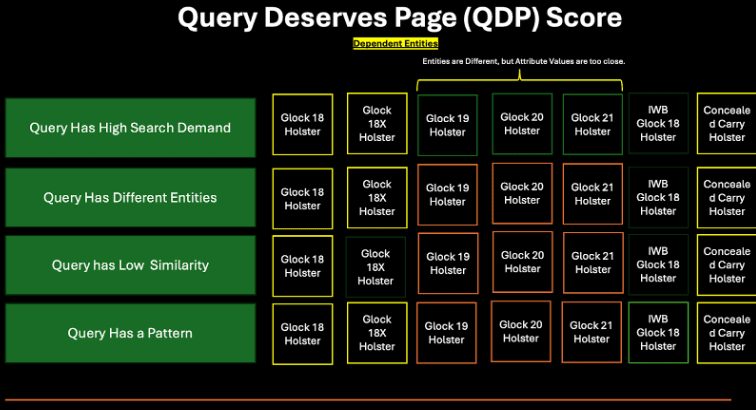
Term-weight calculation is the process of identifying the most dominant term within a query. Once the heaviest term is determined, the search engine can cluster the query accordingly and build an index around that primary meaning. In practical terms, a new index often means the topic deserves its own dedicated landing page. In the example discussed by Dr. Monika Henzinger and Dr. Marc Najork, BERT assigns different weights to the words in a query. For a search such as “Nike running shoes,” which term should lead the interpretation the brand, the product, or the adjective? In this scenario, the brand carries the highest weight, the modifier “running” is secondary, and the product term “shoes” is the lightest component.
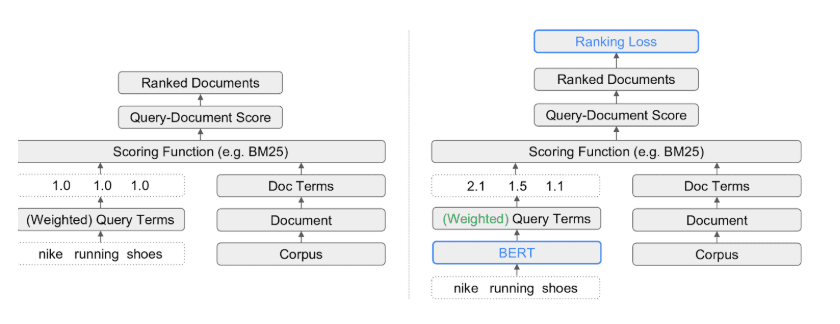
Once term-weight calculation is understood, it becomes clear how to design the contextual vector, page hierarchy, centerpiece annotation, and overall layout. After meeting the query-related criteria for deciding whether a page should exist, the next layer involves index-related criteria. Signals such as average PageRank, document-cluster size, and document-vocabulary similarity strongly influence whether a search engine should open a new index or reuse an existing one. Google evaluates both query statistics and document statistics to decide whether a new index, and therefore a new landing page, is necessary. The same logic applies to AI-generated answers: you can shift AI responses by shaping the document and query statistics that influence co-occurrence and declarative relevance.
If the targeted entity already sits in a cluster with a high PageRank, the search engine is more likely to construct a dedicated index for it. This is why, in casino or payday-loan SERPs, two queries that mean the same thing can produce results that differ by 90%. Because of the high conversion value, publishers create excessive pages and interlink them heavily, which leads to vocabulary divergence, higher average PageRank, and larger cluster sizes. As a result, the semantic distance between two similar queries increases, even though their meaning is the same linguistically. This phenomenon is known as query semantics. For example, while “buy cars” and “sell cars” are logical opposites in everyday language, in the search bar they become near-synonyms and return overlapping intent clusters.

Below, you can see the specific case study with these principles and methodology.
During our Holistic SEO Mastermind in Turkey, we presented this project in detail and shared its 20,000-word Topical Map SOP. The same principles apply to the casino industry. If a slot game has no search demand and no meaningful conversion value, it should not become a standalone page. Instead, it must be placed inside an entity-class page, such as “Best Egyptian-Theme Slot Games.”
This is where our concept of PoS, Page or Segment (not to be confused with part-of-speech tagging) becomes essential. If the topic does not justify a page, it should become a segment. A topical map is not about creating a page for everything it is about organizing contexts, attributes, and documents in a way that reduces retrieval cost and consolidates ranking signals. The same logic applies to reviews: if a game, casino, or sub-topic does not deserve its own page, place it as a section under “Alternatives,” “VS Pages,” or “Best Listicles.” You do not need to open a new page for every small game, machine, brand, or query variation.
This philosophy aligns with what Navneet Pande defined as “site quality”, the idea that a website should minimize low-value URLs and maximize the clarity and efficiency of its structure.

Q: Entities are at the core of Semantic SEO. How can casino sites leverage entities (games, bonuses, providers, jurisdictions) to strengthen topical authority?
A: SEO has two main patterns. Compromising, and Deepening. Meaning that Entities are the backbone of Semantic SEO, because search engines do not rank strings, they rank things. In the casino industry, these “things” are concrete entities like slot games, bonus types, software providers, jurisdictions, payment methods, and player-intent attributes. If a website organizes these entities with the correct relational hierarchy, it lowers the cost of retrieval, strengthens the contextual vector, and makes the source the cheapest and most efficient option to evaluate, rank, and test.
An entity has two fundamental components: attributes and relations. Every attribute naturally creates a relational connection to another entity, which is why a knowledge graph is, at its core, a relational graph. In the casino context, an entity such as a casino inherits lexical semantic relations types of casinos, parts of a casino, and functions of a casino and these relations emerge directly from its attributes.
In Casino SEO, entities also carry commercial attributes and perspective-driven attributes, and each of these attributes leads the entity into new relational paths within the graph. Google ranks perspectives and opinions as much as objective facts, especially after introducing concepts like the language score and the LLM-selection engine in the Search With Stateful Chat and AI Overview–related patents, led by inventors such as Anand Shukla and Srinivasan Venkatachary. This shift proves that Google evaluates not only factual relational data, but also declarative content, human perspectives, and real-world sentiment tied to the entity.
Because of this, it has become more important than ever for Casino SEO websites to reflect a rich, consistent, and relational entity database through their declarations, documents, and semantic connections. By mapping entity attributes and exposing their relations games, bonuses, providers, jurisdictions, payment methods, features, and player-intent vectors a website communicates both knowledge and perspective, strengthening its position within the knowledge graph. In other words, attributes create relations, relations create meaning, and meaning creates rankings. To transform attributes into meaningful assets, you must decide whether each attribute deserves to become a Page or Segment (PoS). Not every attribute should be turned into a standalone URL. When an attribute carries independent search demand, commercial value, conversion potential, and relational depth, it should become a dedicated page a centerpiece or satellite document that can rank, collect links, and generate its own index. However, if the attribute has low search demand, weak commercial weight, or is purely context-supporting, it should remain a segment within a broader entity-class page, such as “Best Egyptian Theme Slot Games,” “Low-Deposit Casinos,” or “MGA-Licensed Casinos.” The purpose of PoS is not to create a page for everything, but to organize attributes into the most cost-efficient index structure reducing retrieval cost, consolidating ranking signals, and strengthening the semantic network. In Casino SEO, this prevents thin-page inflation, doorway-like URL bloat, and index cannibalization, while maximizing momentum and relevance at scale.
Lastly, whether the query requires experience, or expertise, the document should follow a different language-tonality, and structure. Google’s Pathway Language Model always uses a different language model for a different topic, to decrease the cost, and increase accuracy, literacy, uniqueness, and formal efficiency.

Similarly, Google’s AI Mode related search with stateful chat patent mentions that they use a different language model according to the classifier’s result. The LLM selection engine chooses a different language according to the topic’s criterion.
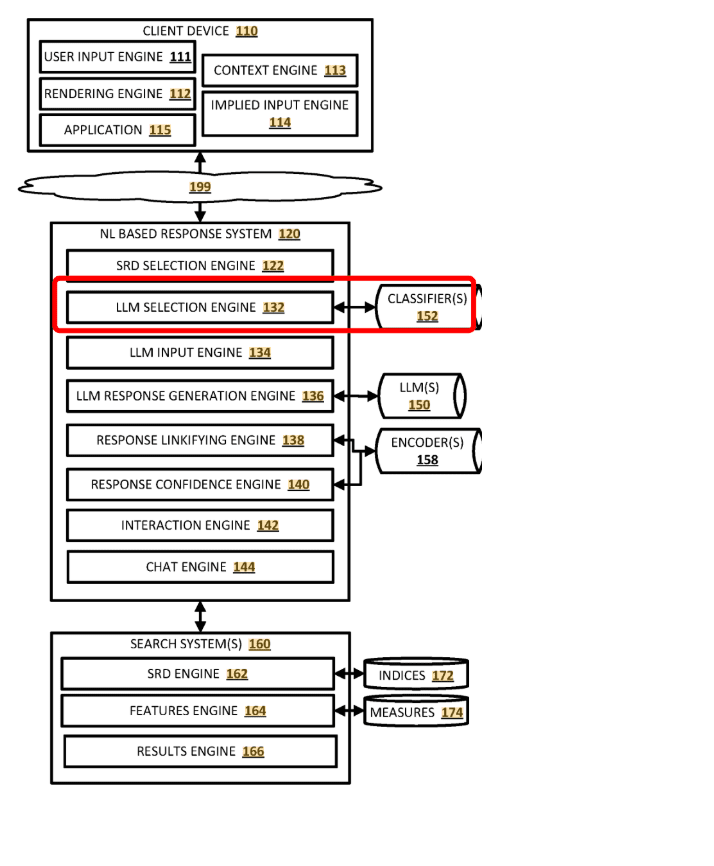
Below, you can see how the search engine uses different “SEARCH DOCUMENT SETS” for creating different types of LLMs, and creation of Natural Language Summaries, by using “measures” for triggering different SERP Features.
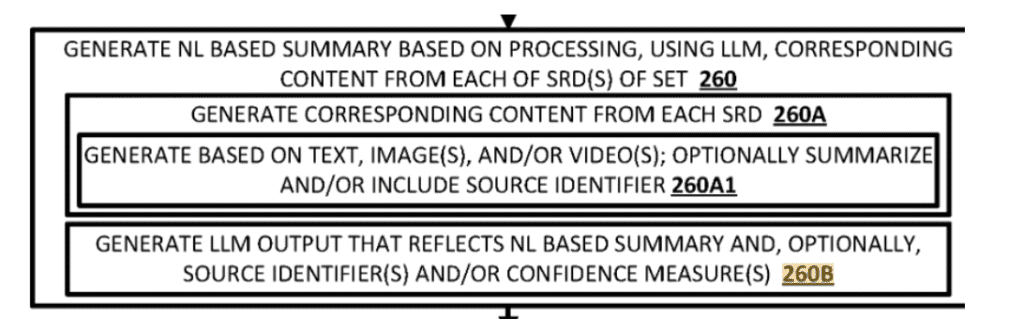
During our “Fundamentals of Information Retrieval” presentation, lecture and speech, we have demonstrated Svalbardi.com’s performance over the last 2 years. Many know this project in terms of outranking the WebMD, Healthline, without using backlinks, with a small e-commerce brand, with only 27 documents. In this case, for 2 years, the company doesn’t have an e-commerce store anymore, and it is linking its competitor, but still it ranks and gets 400,000 organic clicks from these 27 documents that are created nearly 3,5 years ago.

This example is important because we targeted the specific entity “luxury water brand” and covered every attribute through a focused mini–topical map. In this case, we did not prioritize momentum, instead, we applied the depth principle, building a rich contextual layer around a single entity. Below, you can see the AI Answer for the query “the most luxury water brand.” Our website appears in both AI Mode and the organic results, proving that depth alone can be enough to win the SERP when the entity coverage is complete. Notice that Google’s AI Mode does not reference the “taste” attribute when defining a luxury water brand. Attributes such as packaging, story, marketing, and logo are evaluated as closer and more contextually relevant to luxury and pricing, while taste remains a weaker, distant attribute in this entity context.
Therefore, prioritizing an attribute requires more than simply mentioning it. With the right tonality, design, layout, placement, and structured information cards, you must highlight the attribute in a way that aligns with user intent and search engine interpretation. Topical authority is not about “covering everything”, it is about emphasizing the right attributes with the right structure so the search engine can process, rank, and respond to them efficiently. In the slide below, you can see how we leverage visual semantics to represent every attribute and entity within an e-commerce context, ensuring both relevance and responsiveness are maximized.
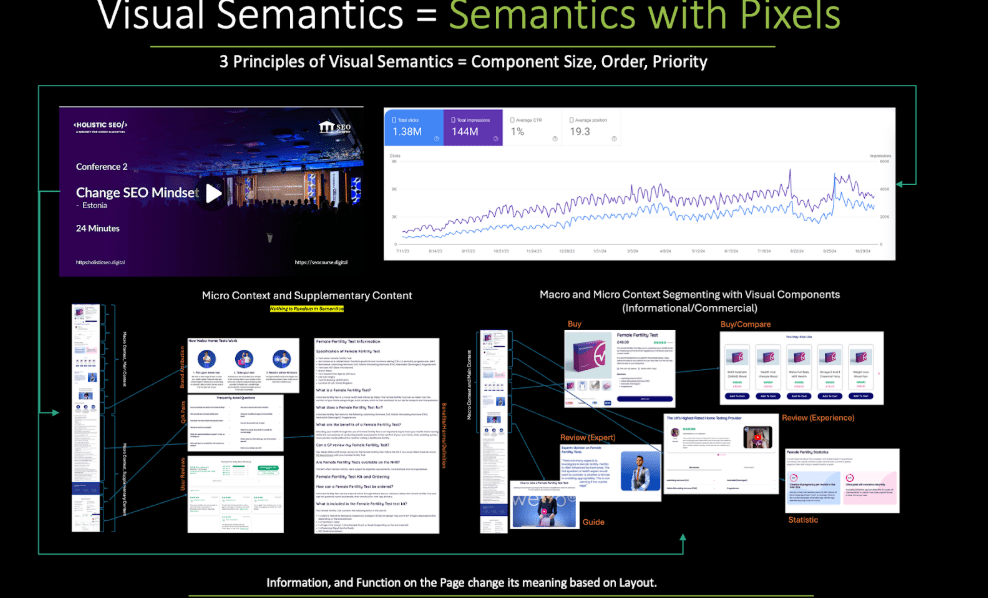
Every attribute of a product or casino should be placed into its own dedicated HTML section, with a clear layout, function, and retrieval purpose. We apply this same structural logic in Local SEO, iGaming SEO, and across every industry, because it allows search engines to interpret entity attributes with greater precision. Likewise, the “structured information card” example from the travel industry follows the same principle, where each attribute is segmented, labeled, and visually distinguished for maximum relevance and clarity.
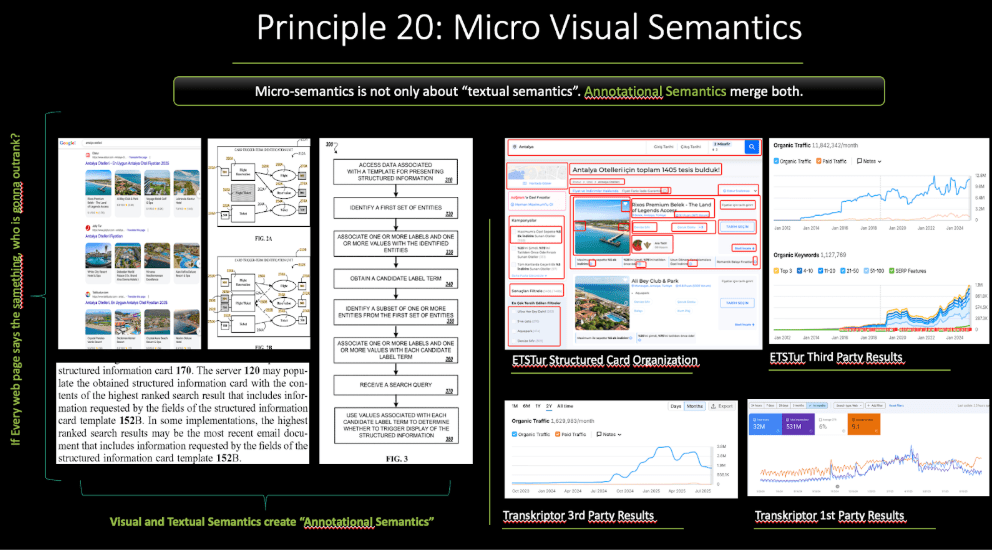
Imagine that these hotel cards are what Google refers to as a “structured information card.” Google evaluates the efficiency of your entity–attribute–value triples using both visual semantics and HTML structure. Now imagine you cover every casino, slot game, or card game entity, but your layout, segmentation, and structured cards are poorly organized. Even with full topical coverage, your relevance will be weaker, because the search engine cannot process or prioritize the information efficiently.
There are advanced methods to increase both relevance and responsiveness by optimizing these visual and structural layers. Here, relevance refers to the information retrieval score, and responsiveness refers to the system’s ability to fulfill the action required by the query. In the iGaming affiliate industry, if the user intent is to ask a question or learn an expert perspective, the interface, layout, and components must reflect that purpose, just as we emphasized with the QnA component above. When structure, intent, and entity signals align, Google rewards the source with higher responsiveness and stronger semantic relevance.
Q: Google’s core updates often shake up the casino SERPs. How can strong topical authority help a site remain resilient when updates hit?
A: The entire strategy of Topical Authority is rooted in Broad Core Algorithm Updates (BCAUs). I realized early on that even when competing with the strongest authority in a niche, you only need to win three core updates in a row to surpass them. If your website wins three BCAUs in a year, assuming those updates affect your website type and industry, you can outrank the most established competitors. For this reason, the primary objective always remains the same: win the BCAU.
In practice, we predict the timing of the next core update by analyzing the historical cycles of previous ones. For example, based on current patterns, we expect the next BCAU to fall between 18 and 25 November. Because Google does not heavily use the final 15 to 20 days of data before an update, we make all major changes at least 15 to 20 days in advance. This allows the system to process the new signals before the evaluation window closes. This timing is one of the reasons we consistently win core updates.
However, winning once is not enough. If you fail to update your semantic content network over time, based on semantic distances, new information, and entity expansions, your content becomes outdated. This is why we operate with a simple rule: every document must be updated at least once every six months. Topical Authority is not a one-time achievement. It is an always-on system for maintaining the most complete, accurate, and deeply connected relational database on the web, at the lowest cost of retrieval.
- During our Fundamentals of Information Retrieval keynote, we demonstrated this through Svalbardi.com. Many people know the case: outranking WebMD and Healthline without backlinks, using only 27 documents. Even though the company shut down e-commerce two years ago and now links to a competitor, the site still maintains 400,000 organic clicks from content that was first published 3.5 years ago. That is the compounding effect of Topical Authority.
- The same applied to Xometry.com, where we scaled the website from 0 to 600,000 monthly clicks and helped contribute to a 167% increase in stock price. When we stopped updating older documents, the site lost some ground during subsequent BCAUs, yet it still retains nearly 75 percent of its gains. The lesson is consistent across every project: a solid semantic foundation combined with continuous updates is necessary for long-term success. There is no permanent one-time solution in SEO. The only durable strategy is constant improvement aligned with core update cycles, supported by a maintained semantic network and historical trust signals. You can see one of our slides that says “Never feel sad, or happy” which explains the “how stoic you should be in SEO”.

Q: AI is transforming content creation. Do you believe AI can accelerate building topical authority in the casino niche, or does it risk producing too much low-value duplication?
A:
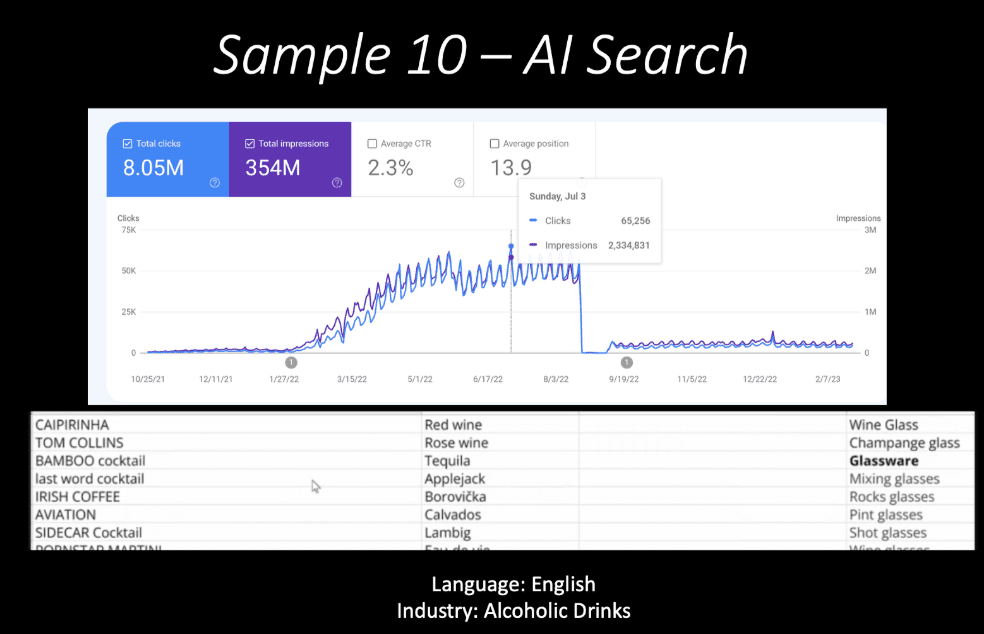
- We launched our first AI projects in 2021. Below is a slide from my 2023 Saigon speech, showing an AI-driven cocktail project that scaled to 65,000 clicks per day. Eventually, it received a manual penalty. After that experience, and after losing several other AI-driven websites that had between 2 million and 60 million monthly clicks, we shifted our philosophy.
- Since then, we have used AI primarily for research and quality assessment, rather than for direct content production. This is why I emphasize concepts such as contentEffort, LLM-selection engine, and total human effort as signals that search engines can use in their quality evaluations.
- In our view, AI can support content creation, but only with strong human supervision and editorial control. It is useful for accelerating content refresh, closing the logistical gap with competitors, and supporting micro-contexts. However, I would never use AI for center-piece annotations or above-the-fold content, where expertise, originality, and experience are critical. AI should be limited to supplementary areas and used cautiously.
- Today, we use more than 200 GPT-based agents to speed up various processes, including triple analysis, medical research assistance, and predicate gap closing. But the final writing always comes from human experts, not AI. The specific slide from the Saigon 2023 is below.
Even if Google doesn’t punish an AI-heavy or AI-blended website initially, it is possible to get some certain level of “blocking” in the rankings. Thus, either being extremely cautious, or using it very lightly is better.
Q: If you had to design the “perfect” topical authority strategy for a new casino site today, what would be its first three building blocks?
A: A Topical Map has five fundamental components: the central entity, the central search intent, the core section, the outer section, and the source context. The source context defines what the website represents, and based on this, Google classifies the entire web entity. For example, a casino affiliate website and a casino brand website cannot share the same layout, structure, or semantic SEO strategy for ranking the same queries.
The central search intent represents the primary action that shapes the entire semantic content network. The central entity is the main entity that appears throughout every macro-context and micro-context across the entire network of documents.
The outer section targets queries that require stronger historical data, while the core section focuses on consolidating ranking signals for monetization-oriented pages. If the building blocks represent the sections of a topical map, and the source context is a “casino brand” rather than a “casino affiliate,” then the first segments must be built around “casino games,” “game rules,” and “game comparisons.”
To protect the project, the slide below shows only a portion of the full structure. The complete model consists of five essential stages for launching a semantic content network:
- Creating the topical map
- Creating content briefs
- Creating the documents
- Creating the mock-up design
- Creating the professional Figma design, coding it, placing the content, and launching the website

The main goal is not simply opening three building blocks such as “games,” “game rules,” and “game comparisons.” What truly matters is how these groups of attributes and contexts are organized as letters, pixels, and bytes in order to accumulate historical data. The most critical task is to structure the five fundamental components of the topical map correctly from the start. This includes planning both the core and outer sections, along with their design elements, components, and entity distribution based on contextual relevance.
For a poker-focused casino project, the primary entity-attribute pairs would include “poker rooms,” “live poker,” “poker types,” “poker rules,” “poker tournaments,” “poker cards,” and “poker hands.” These must be combined and interconnected through term-weight calculations, structured information cards, and macro-micro context segmentation. Distributing relevance across the network in a systematic way is essential for building a durable and semantically strong topical authority.
Conclusion
Interviewing Koray Tuğberk GÜBÜR is like taking a step into the mind of a search engine. He doesn’t just talk about SEO, he dissects it. Every concept, from topical authority to entity mapping, becomes part of a larger system built on logic and experimentation.
What stands out most is his view of topical authority not as a trend, but as the foundation of sustainable rankings. In Koray’s world, authority isn’t earned through keywords or backlinks alone; it’s built through structure, clarity, and the efficient organization of knowledge. When Google’s algorithms evolve, the sites that survive are those that think like Google: efficient, consistent, and semantically connected.
The casino industry, with all its volatility and competition, is the perfect testing ground for this philosophy. It exposes weak systems instantly — yet it also rewards precision and discipline faster than any other niche. Koray’s approach has proven that when content, entities, and structure work in harmony, even the most difficult SERPs can be conquered.
His insights also carry a quiet warning. As AI floods the web with low-value duplication, the true winner won’t be who publishes the most, but who builds the most trustworthy and structured content network. SEO isn’t a guessing game or a checklist; it’s an ecosystem.




