SEO measurement is entering a new era as large language model (LLM) tools reshape how people search, discover, and interact with content. Traditional metrics like organic traffic and rankings still matter, but they no longer tell the whole story. In the old world of SEO, the question was simple: “Where do I rank?” In the age of generative AI, the more important question is: “Am I the answer?”
With AI-driven search, users often get responses instantly—without ever clicking through to a website. SEOs now need to measure both: the classic KPIs that track business growth (traffic, conversions) and the new generative metrics that reveal AI trust and authority. In this guide, we’ll break down the core Generative SEO KPIs and show you how to measure them—using both available tools and practical manual methods.
Key Statistics About This Topic
- Some experts estimate that by the end of 2025, over 70% of searches could result in no external click, largely due to the growth of AI-powered answers.
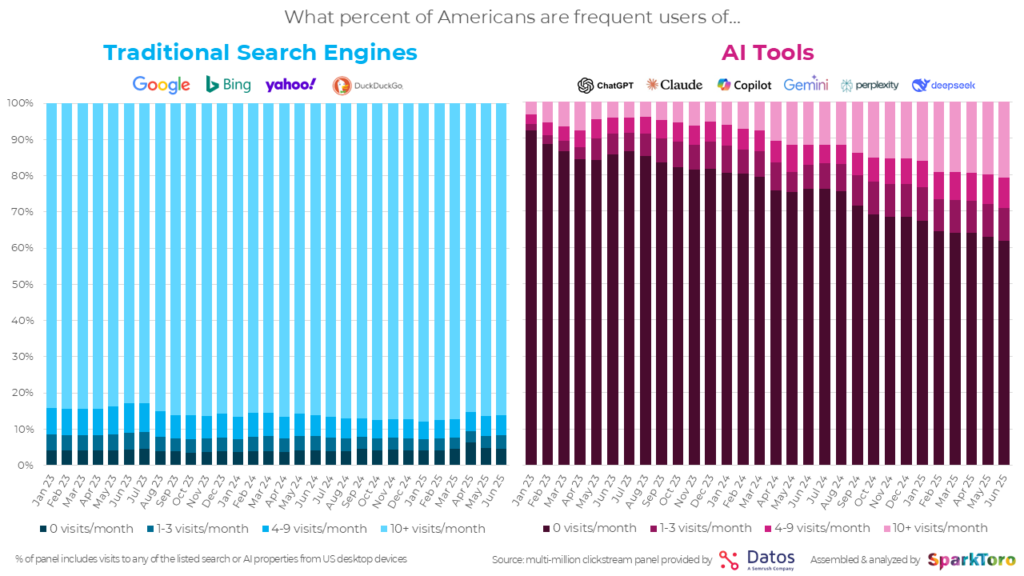
- According to Sparktoro, “Over 20% of Americans are now heavy users of AI Tools (employing them 10X or more each month), and nearly 40% use one AI tools 1X+/month. Despite this massive growth, traditional search engines aren’t going anywhere: 95% of Americans continue to use them each month, and 86% are heavy users.”
Key Takeaways
- Despite the hype, LLM tools aren’t replacing search — in fact, data shows that even committed ChatGPT users end up running more Google searches than before.
- New metrics show influence in zero-click and AI-driven search environments.
- Success is measured by how AI uses and cites content, not just clicks.
- Tracking semantic relevance and AI citations reveals real visibility.
- Some traditional SEO metrics remain highly relevant and should continue to be part of any KPI framework.
Why Clicks Are Less Relevant in AI Search
Clicks matter less because many AI systems deliver answers directly without showing traditional links. People get quick, synthesised responses powered by language models like GPT-4 or Claude. This results in zero-click search experiences where users don’t visit external sites.
Rather than chasing clicks, modern SEO strategies now focus on AI attribution rates—how often a brand’s content is cited in AI-generated answers. Success is no longer just about ranking alone; it’s about whether AI systems can understand, trust, and use your content as part of their responses.
Core Generative SEO KPIs
Measuring success in this new landscape means looking beyond clicks and rankings, which no longer tell the whole story. Generative SEO requires fresh KPIs that track how often content is retrieved, how relevant it is, and how frequently it’s cited in AI-generated answers. Here are the core metrics that now matter most in the age of AI search:

1. AI Citations
AI Citations happen when generative tools directly reference – link your content in their answers. Unlike traditional mentions, these signal that AI views your content as trustworthy, authoritative, and relevant.
Why it matters: In generative search, citations are the new rankings. If AI links you, it means you’re being recognized as a trusted source.
Example: Here’s how it looks in practice—Search Engine Land’s article about SEO linked by ChatGPT Search when a user asks, “What is SEO?”
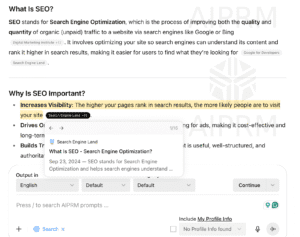
AI Citations Example
Tool to Track:
SE Ranking – AI Results Tracker
Tracks whether your website is directly cited and linked in Google AI Overviews, Bing Copilot, and Perplexity AI.
Shows which queries produce citations, how often your site is linked, and how this changes over time.
How to Track AI Citations Manually
Until tools are more advanced and cheaper, you can check citations yourself.
Run Queries – Search in Google AI Overviews, Bing Copilot, or Perplexity using terms relevant to your site, like “best SEO tools for small businesses.”
Check for Links and Citations– See if your site appears as a clickable link, footnote, or a part of your content. Count it only if your URL is included.
Record Results – Log the date, platform, query, cited URL, and where it appeared in the answer in a simple spreadsheet.
2. AI Overview Impressions
AI Overview Impressions track how often your site appears inside Google’s AI Overviews—the summaries generated at the top of search results. Each impression counts when your page is shown as a linked source, whether or not the user clicks.
Think of it like regular search impressions in Google Search Console, but limited to AI-powered results.
Why it matters: Even without a click, appearing in AI Overviews increases your visibility and builds brand trust.
Example: If someone searches “What is AI overview”, the following sites are listed in Google’s AI-generated card as a trusted source.
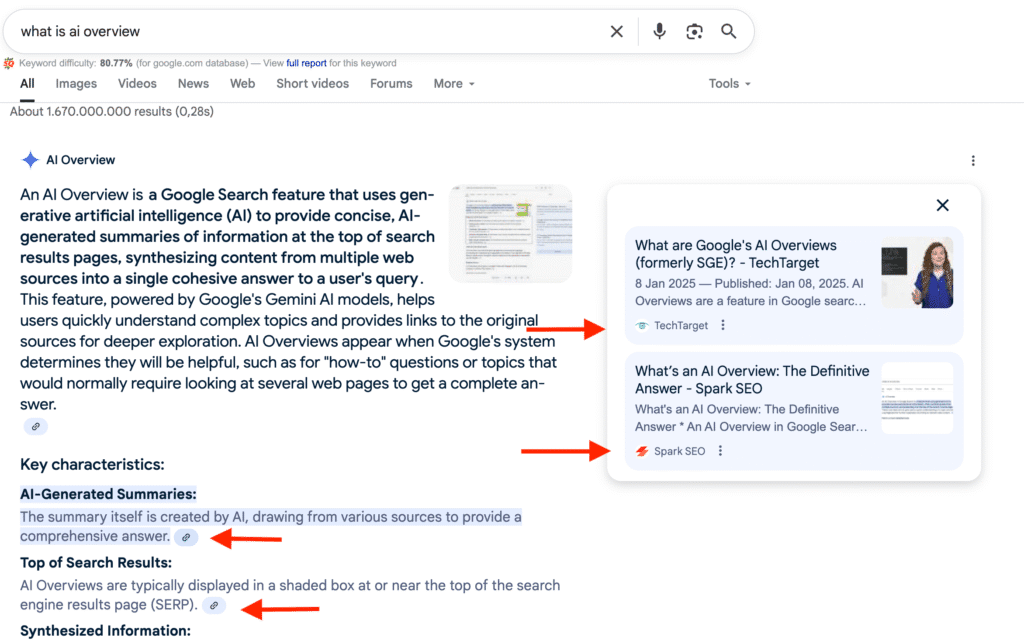
AI Overview Impressions Example
Tool to Track:
Tracks when your site appears in Google AI Overviews.
Reports the queries, frequency of impressions, and whether your site earned a link.
How to Track AI Overview Impressions Manually
Run Searches Regularly
Search Google for target queries where you want visibility.
Example: “SEO trends 2025.”
Check the AI Overview Section
See if Google’s AI Overview appears.
Look for your site in the sources linked below the AI summary.
- Document each impression with a date in a sheet
3. Zero-Click Visibility
Zero-Click Visibility happens when your content is shown in search results generated by LLM tools, but users gets the answer directly on the page without clicking through to your site.
It often appears in features like:
Google AI Overviews (SGE)
Featured Snippets (direct answers at the top)
Knowledge Panels
People Also Ask (PAA) boxes
Local Packs / Maps
Why it matters: Zero-click doesn’t mean zero impact—your brand still gains authority, visibility, and recognition.
Example: If someone searches “What is GEO?” Google’s AI might display your definition directly, so users see your brand even if they don’t visit your site.
Tools to Track:
Semrush – SERP Features Tracking
- Tracks if your site appears in featured snippets, People Also Ask, knowledge panels, local packs, etc.
- Shows which keywords trigger zero-click results and whether your site is included.
Google Search Console (Indirectly)
- Doesn’t label “zero-click” directly, but you can spot it by:
- High impressions
- Low click-through rate (CTR)
- Usually linked to queries where Google answers the question right in the SERP.
How to Measure Zero-Click Visibility Manually
If you don’t want to rely only on tools, here’s the step-by-step:
Choose Target Keywords
Example: “SEO meaning”
Search Them on Google
Look at the search results page.
Check if your site appears in zero-click features
Record Findings in a Spreadsheet
Keyword
Zero-Click Feature Type
Position (e.g., snippet, PAA #2, map result #1)
Impressions vs Clicks (from GSC, if available)
Compare Over Time
Repeat checks monthly.
Track if you’re gaining or losing visibility in zero-click spots.
4. Embedding Relevance Score
Embedding Relevance Score measures how closely the meaning of your content matches what a user is searching for.
Instead of focusing only on keywords, LLM systems like Google AI Mode use embeddings—mathematical models that represent words, phrases, or even whole pages—to understand context and intent.
The score is usually shown on a scale from 0 to 1 (or 0–100). The higher the number, the more semantically relevant your content is to the query
Why it matters: Unlike keyword matching, embeddings reward content that explains topics naturally, with depth and context.
Example: A page about “AI-driven optimization” could still be surfaced for a query like “how to improve content for generative search” because AI sees the shared meaning, even if the exact keywords differ.
Tools to Track:
Uses semantic analysis to score how well your content matches top-ranking pages.
Its Content Score is essentially an embedding relevance score — higher = more semantically aligned with the query.
AI & Vector Tools (Advanced)
Tools like OpenAI Embeddings API or Pinecone, let you measure cosine similarity between a search query and your content.
This gives you a numeric score (0–1) showing how close your content’s meaning is to the search intent.
5. Chunk Retrieval Frequency
Chunk Retrieval Frequency measures how often small sections of your content—called chunks—are pulled and reused by AI systems like Google AI Overviews, Bing Copilot, or Perplexity.
A chunk could be a paragraph, a FAQ, or even a short product description. Since AI doesn’t usually use an entire page, it breaks content into smaller pieces and selects the parts that best answer the query.
The frequency shows how often those chunks are chosen and surfaced in AI-generated results.
Why it matters: If your chunks are reused often, it signals that AI sees your content as especially valuable.
Example: Your FAQ “What is Generative SEO?” could be pulled by Perplexity dozens of times across related queries.
Tool to track:
I haven´t found any tool that can do this 100% at the moment. Let me know if you are aware of any SEO tools that can track those.
How to measure manually
Run relevant queries in AI search tools and note when parts of your content (not the whole page) appear. Keep track in a spreadsheet. This is quite a big manual job, and I hope that it can be automated with tools in the near future.
6. Vector Index Presence
Vector Index Presence measures whether your content is stored in an AI’s vector database—its version of “memory.” If your content isn’t vectorized and crawlable, AI systems can’t access or use it in responses.
Why it matters: If search engines can’t parse your content because of poor crawlability or missing structure, you’re effectively invisible to AI.
Example: A blog hidden behind heavy JavaScript may never be processed correctly, meaning it won’t appear in AI-generated answers.
Tools to track:
llms.txt Validator (for example, https://mrs.digital/tools/llms-txt-validator/ – confirms your site allows AI crawlers.
Schema.org validators – ensure structured data is applied correctly.
7. LLM Answer Coverage
LLM Answer Coverage measures how many different queries your content is able to answer in AI-driven search systems.
Why it matters: The more queries your content supports, the stronger your topical authority. Broad coverage shows that your site is seen as a reliable, go-to source across an entire subject area—not just for one keyword.
Example: A single blog post about “AI SEO tools” might also appear in AI-generated answers for:
“How to automate SEO with AI”
“What are the best AI SEO platforms 2025”
Tool to track:
Semrush Breakdown by Question– tracks questions of you and your competitors for multiple queries.
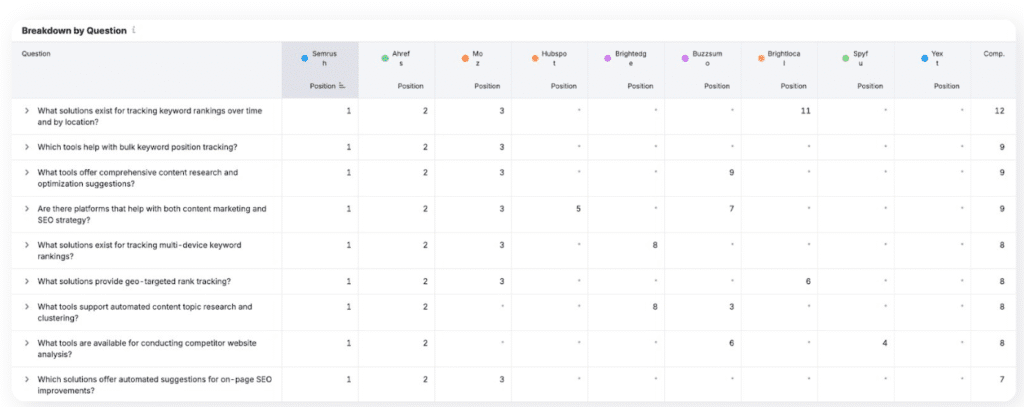
8. Brand Mentions
Brand Mentions track how often your brand is referenced across the web—whether linked or unlinked. AI systems treat these mentions as signals of authority and trust.
Why it matters: Building credibility today goes beyond backlinks. In fact, some say that mentions are the new backlinks! Mentions in news articles, forums, and social media all strengthen your authority in the eyes of both users and AI search engines.
Example: A Reddit discussion about “SEO in 2025” highlights your brand. Even without a link, AI engines recognize it as proof of credibility.
Tools to track:
BuzzSumo – monitor mentions across PR, news, and social channels.
Google Alerts, Ahrefs Mentions Alerts, Semrush Brand Monitoring – track both linked and unlinked references.
How to measure: Keep track of the volume and sentiment of brand mentions. Positive coverage across trusted sources increases your brand’s authority and boosts the likelihood of being cited by AI.
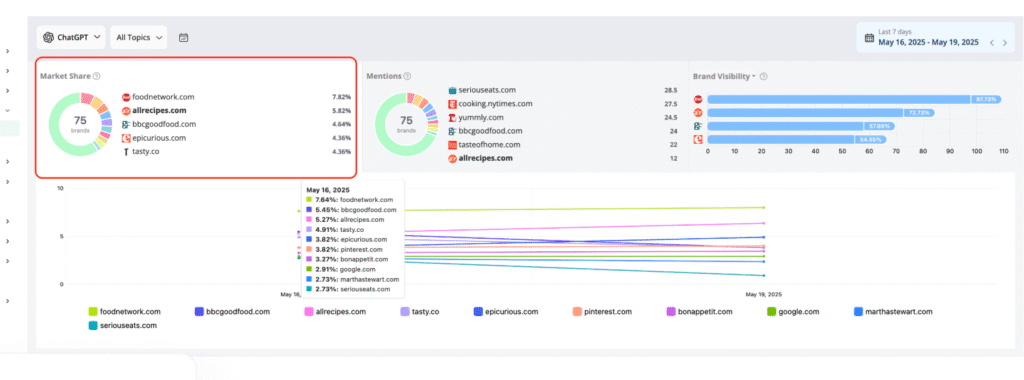
9. AI Visibility Share (Competitive KPI)
AI Visibility Share is the percentage of times your website appears in AI-generated search results (like Google AI Overviews, Bing Copilot, or Perplexity) compared to the total appearances across your competitors.
It shows how much visibility your site has in AI search answers within your niche.
Why It Matters: It’s the generative equivalent of share of voice — who dominates AI’s answerscape. Example: For “SEO automation tools,” your brand is cited in 25% of answers; your competitor owns 50%.
Tool to Track:
- For example, Adwance Web Ranking calls it Market Share:
How to Measure AI Visibility Share Manually
Step 1: Define Target Queries
List important keywords in your niche (e.g., “AI SEO tools 2025”).
Step 2: Test Them in AI Search
Run each query in Google AI Overviews, Bing Copilot, Perplexity.
Note whether your site is cited as a source.
Step 3: Track Competitors Too
For each query, record which competitors appear in the AI answers.
Step 4: Calculate Visibility Share
Formula:
AI Visibility Share (%) tells you what percentage of all AI citations in search results belong to your website.
You calculate it by:
Counting how many times your website is cited in AI-generated answers across all the queries you track.
Dividing that by the total number of citations (yours plus your competitors’) across those same queries.
Multiplying by 100 to get a percentage.
Bonus KPI: Referral Traffic from AI Search
Referral Traffic from AI Search tracks the number of visitors who click through to your site directly from AI-powered platforms, such as Google AI Overviews, Bing Copilot, or Perplexity.
Why it matters: While much of generative search happens in a “zero-click” environment, referral traffic proves that AI-driven visibility can also send highly engaged visitors to your site. These users often arrive with strong intent, since they’ve already seen your content cited in the answer.
Example: A user reading an AI Overview about “best SEO tools” clicks the link to your guide, driving targeted traffic to your site.
Tool to track:
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) – monitor traffic sources and segment by AI-related referrals.
The Classic SEO KPIs That Are Still Relevant
Traditional search isn’t being replaced by AI—data shows that even heavy ChatGPT users actually increase their Google searches over time. Success in the AI era means tracking both sets of KPIs: the new generative ones and the traditional metrics that still matter. Here are the top 4 classic SEO metrics that should be for sure included in your SEO KPIs methodology:
Organic Traffic
The backbone of SEO reporting. Monitoring visits from organic search shows whether your optimization efforts are increasing visibility. Segment by branded vs. non-branded queries for deeper insights.Keyword Rankings
Rank tracking is evolving, but still valuable. Instead of obsessing over single keywords, monitor groups of keywords around core topics to assess topical authority.Conversions (Leads, Sales, Sign-Ups)
The ultimate KPI. SEO is only meaningful if it supports business growth. Tie organic traffic to form fills, purchases, or subscriptions to prove ROI.Engagement Metrics (Time on Page, Bounce Rate, Scroll Depth)
These metrics reveal how well your content satisfies user intent. If visitors stay longer, scroll further, and engage more deeply, it’s a clear signal that your content is valuable—both to users and to AI systems learning from behavior.
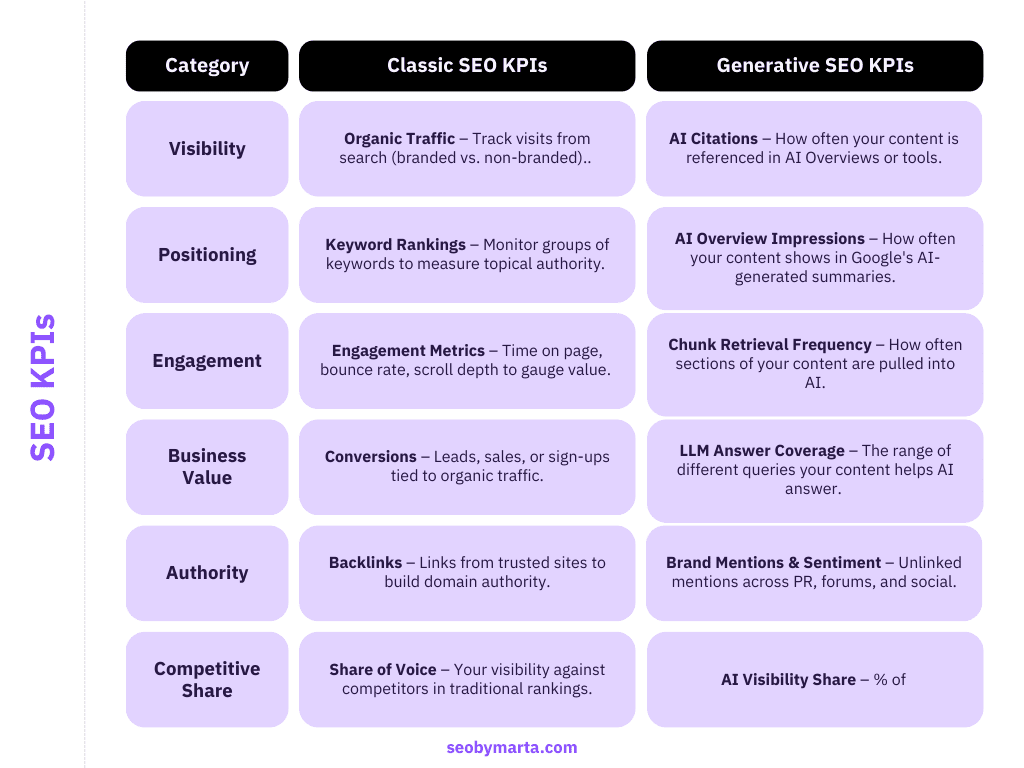
Classic and generative SEO KPIs
Goal Setting and Continual Optimization
Setting specific goals for generative SEO helps measure progress in a changing landscape. Goals should focus on increasing AI citations, enhancing content clarity for AI synthesis, and improving positive sentiment in AI answers.
Key practices include:
- Choosing your own core KIPs from the list presented above (even 4 or 5 of them is enough for the start) and combining the classic ones with the new generative KPIs
- Benchmarking current AI visibility to set realistic targets
- Setting up goals for the next 3, 6 and 12 months
- Documenting the starting point data and the changes per month per KPI (including the biggest optimisation points), is essential
Continual testing and refinement of your SEO work based on AI feedback ensures that your website remains relevant and authoritative in generative search results.





