Generative AI search and features like Google’s AI Overviews are rapidly reshaping how users find and interact with content—especially as summary-based results rise. While traditional search (particularly Google) remains dominant, the hidden power of AI answers is already disrupting click-through rates and organic traffic. For content creators and SEOs, this is still a decisive moment as optimising for visibility now requires adjusting strategies for AI-powered platforms, not just classic SERPs. In this guide, you’ll learn how to optimise content for AI-driven search engines, increase citation potential, and maintain visibility in the era of generative search.
Key Statistics About This Topic
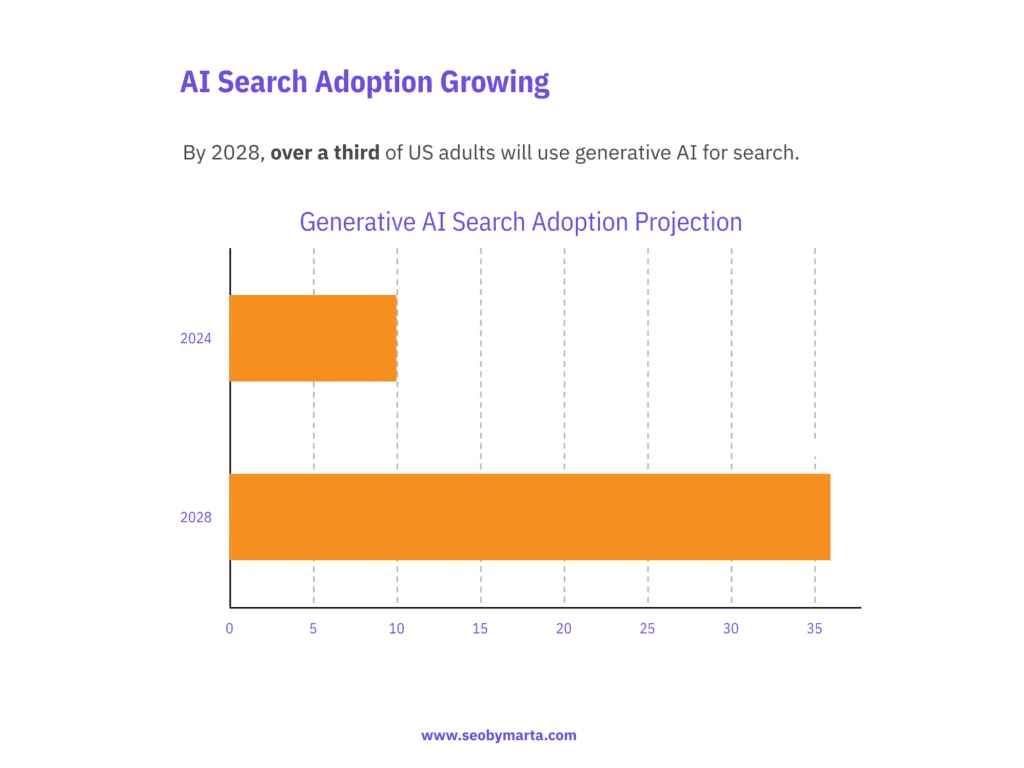
- Search behaviour projections: In the U.S., 36% of adults are expected to be using generative AI for search by 2028
- The Rise of Google AI Overviews:
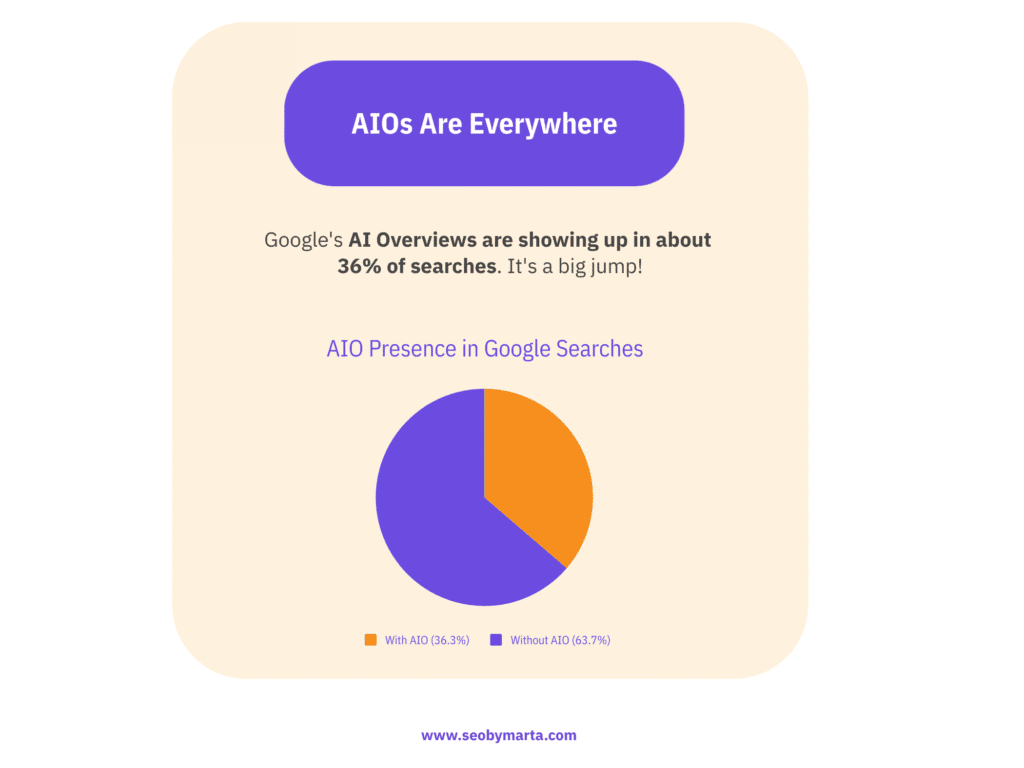
AIOs appear in approximately 36.3% of Google searches. Since March 2025, AIO inclusion has grown 115%, and the share of keywords triggering AIOs has doubled.
- Organic Traffic loss:
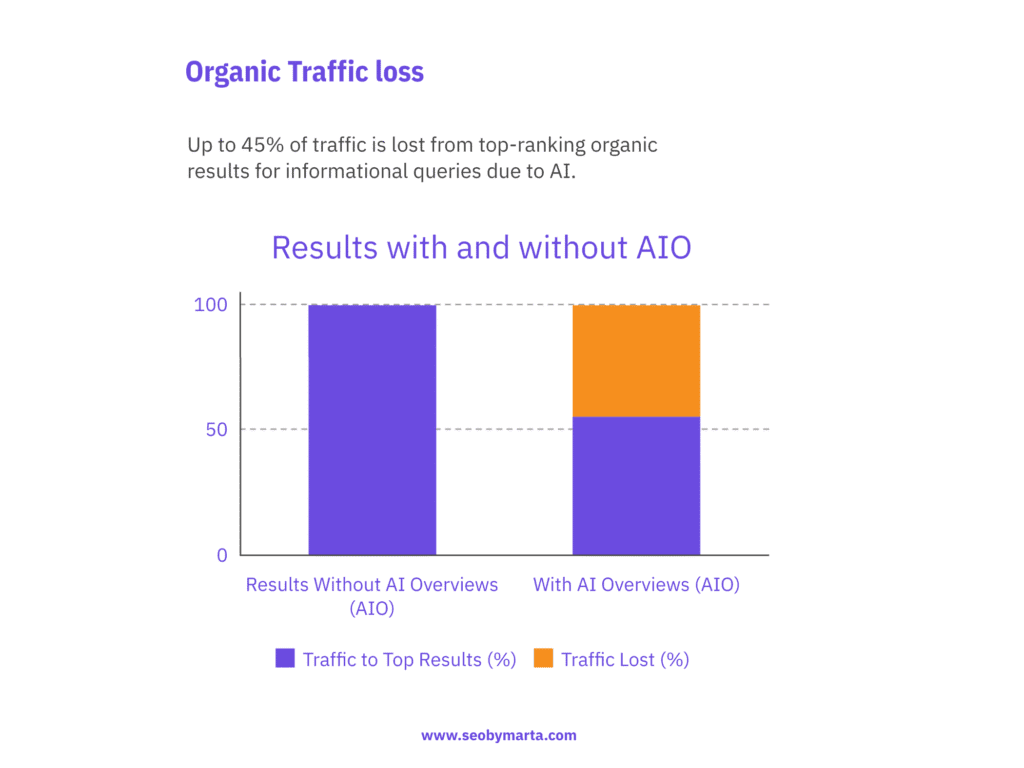
Up to 45% of traffic is lost from top-ranking organic results for informational queries due to AI.
-
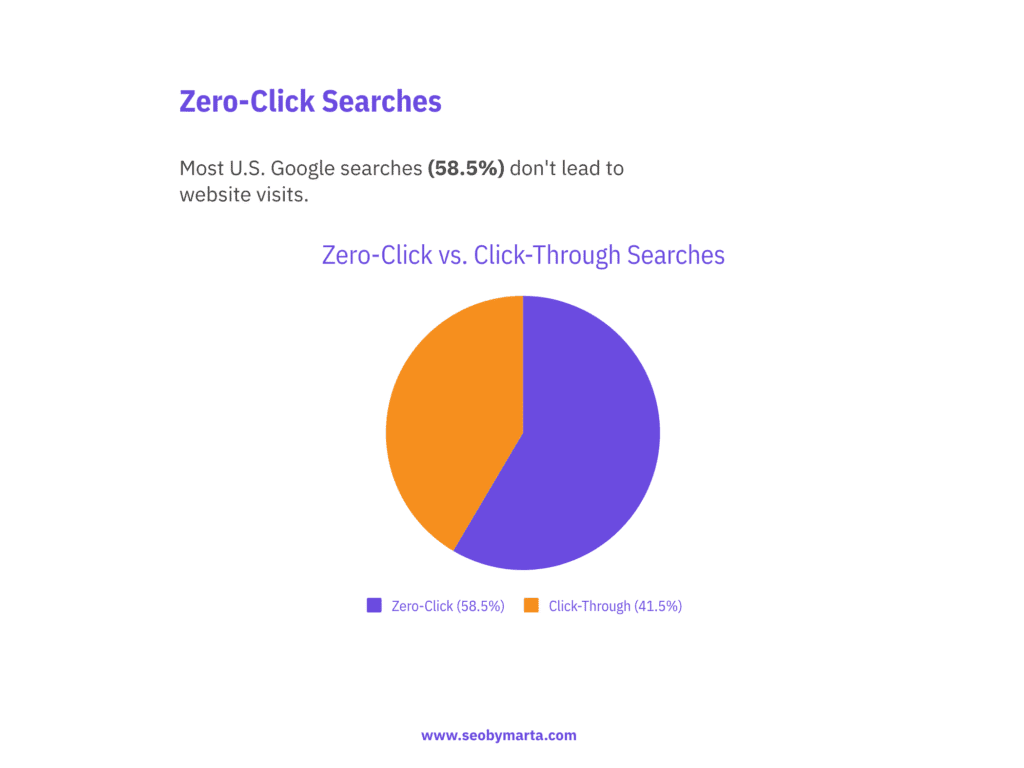
Zero-click searches are sky-high: 58.5% of U.S. Google queries result in no clicks to websites. This means over half of searches end without users visiting external pages.
Key Takeaways From This Article
-
- Content must be structured clearly with direct answers and a proper technical setup to work with AI systems
-
Implementing schemas and proper technical setup improves visibility in generative search results.
-
Demonstrating real expertise through author bios, case studies, or unique insights strengthens trust and authority.
-
Building topical clusters and measuring AI-driven performance require different methods than standard SEO.
How Generative AI Search Engines Work
Generative AI search engines operate through large language models (LLMs) that process queries and generate human-like responses. Unlike traditional search engines that match keywords to web pages, these systems understand context and intent.
When a user asks a question, the AI model analyzes the query and draws from its training data. The system then creates a complete answer by combining information from multiple sources. This process happens in seconds through complex neural networks.
Key Components:
-
- Natural language processing for query understanding
-
- Knowledge synthesis from multiple data sources
-
- Real-time answer generation
-
- Source attribution and citations
The AI models continuously learn patterns in language and information. They can handle follow-up questions and maintain conversation context. This makes the search experience more interactive than traditional methods.
The Role of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
GEO differs from traditional SEO by focusing on AI citation and visibility rather than click-through traffic. Success is measured through AI presence metrics, not organic traffic rankings, requiring new strategies for digital marketing professionals.
AI tools are not replacing Google- they just expand the Search. The Generative search isn’t replacing SEO—it’s reshaping it. Traditional ranking factors still matter, but clarity, structure, and authority now play a bigger role in whether AI tools choose your content for answers. By combining strong SEO foundations with AI-friendly practices, brands can secure visibility across both search engines and the new wave of generative platforms.
Optimising Content for AI Discoverability in 10 Steps
Step 1: User Intent Matching
Understanding user intent forms the foundation of effective AI content creation. Content writers must analyze and understand what users truly want when they search for information:
- Research common questions in your industry. Tools like Google Search Console show actual queries people use. Create content that directly answers these questions.
- Test your content against real user questions. Ask yourself: “Does this content solve the user’s problem completely?” If not, add missing information or restructure the approach.
Step 2: Section-Based Content Organization
Content for AI works best when divided into independent, self-contained sections. Each section should focus on one specific topic or concept. AI systems don’t analyze entire pages at once. They extract individual chunks of content to answer user queries. This means every section must make sense without requiring context from other parts of the page.

Structure each section with these elements:
-
- One clear concept per section
- Standalone readability
- Keep related information together in one focused chunk
- Use H2 or H3 that describe exactly what each section covers. Avoid vague titles like “Getting Started” Instead, use specific phrases like “How to Write Articles” or “Common SEO Audit Mistakes”
- Use a relevant subheading that describes the content
- Test each section by reading it alone. If it needs other sections to make sense, restructure the content to be more self-contained.
Step 3: Bullet Points and Lists
Formatted lists help AI systems parse and categorize content accurately. These elements act as signals that guide content extraction.
Bullet points work well for:
-
- Step-by-step instructions
-
- Feature comparisons
-
- Key benefits or advantages
-
- Quick reference information
Numbered lists are better for:
-
- Sequential processes
-
- Ranked items
-
- Priority-based information
-
- Tutorial steps
Format lists properly with HTML markup. Use <ul> and <li> tags for bullet points, and <ol> tags for numbered lists. This helps AI systems understand the relationship between list items.
Keep list items concise and focused. Each point should contain one main idea that stands alone. Don’t overuse lists and bullet points in your content; use them naturally.
Step 4: Strategic Internal Linking
Strategic internal linking helps AI systems understand content relationships and topic authority across your site. Links should connect related concepts and provide additional context. Link to relevant pages when mentioning related topics. Use descriptive anchor text that explains what the linked page contains. Avoid generic phrases like “click here” or “read more.”

Step 5: Use Conversational Language
Natural language queries reflect how people speak and ask questions. Content creators should optimize for conversational search patterns rather than rigid keyword structures. Write in a conversational tone that mirrors how people talk. Use phrases like “how do I” or “what’s the best way to” in headings and content.
Include question-based subheadings that match common speech patterns. Instead of “Email Marketing Benefits,” use “Why Does Email Marketing Work Better Than Social Media?”
Structure sentences to flow naturally when read aloud. AI systems analyze content for natural language patterns and favor content that sounds conversational.
Use long-tail keyword phrases that people say. “How to fix a leaky faucet” performs better than “faucet repair” for AI-generated answers.
Create FAQ sections that address specific spoken queries. These sections help AI systems understand your content’s relevance to user questions.
Step 6: Providing Comprehensive and Direct Answers
AI systems prioritize content that provides complete, actionable answers to user queries. Comprehensive content performs better in AI-generated responses than surface-level information. Start each piece with a direct answer to the main question. Place the most important information in the first paragraph, where AI systems can easily find it.
Write sections that answer specific questions directly:
For example, “What is an Online Casino?” should have its dedicated section (heading H2, for example) with a complete definition and key details. Do not start answering the question with an introduction. Answer the question directly and within the first sentence. How-to content should, if necessary, include step-by-step instructions with specific details. Add contextual information that helps users understand why each step matters.

Step 7:Real-world Applications and Examples
Provide examples and real-world applications for abstract concepts. If explaining SEO, show specific examples of optimized titles and meta descriptions. Include related information that users might need (like in this article). For a “how to bake bread” article, mention common troubleshooting issues and ingredient substitutions.
Step 8: Using Author Bios and E-E-A-T Signals
Complete author bios provide AI models with crucial E-E-A-T signals that establish content credibility. Writers should include their educational background, professional experience, and relevant certifications directly on their content pages.
AI systems scan for specific credentials that match the content topic. A financial article requires authors with finance degrees or industry experience. Medical content needs writers with healthcare backgrounds or certifications.
Key elements for strong author bios:
-
- Professional titles and current positions
-
- Relevant education and certifications
-
- Years of experience in the subject area
-
- Previous publications or media appearances
-
- Contact information and social media links
The bio should appear prominently on each piece of content. Many sites place author information at the top or bottom of articles with a photo and a detailed description.
E-E-A-T signals extend beyond basic credentials. Authors should link to their professional LinkedIn profiles, published works, and speaking engagements. This creates a web of authority that AI models can verify and value.
Learn more about the topic of how to dominate AI search with E-A-A-T in this Video:
Step 9: Citing Reputable Sources and Original Research
Proper citation practices signal content quality to AI systems that evaluate source credibility. Writers must link to authoritative sources like government agencies, academic institutions, and established industry publications.
Original research carries significant weight with AI models. Studies, surveys, and data analysis from the content creator provide unique value that search engines prioritize.
Preferred source types for citations:
-
- Government websites (.gov domains)
-
- Academic journals and universities (.edu domains)
-
- Industry reports from recognized organizations
-
- Peer-reviewed research studies
-
- Official company data and statistics
Each factual claim needs a verifiable source. AI systems check these links to confirm information accuracy. Broken or unreliable sources hurt content authority scores. Writers should quote directly from sources when possible. This allows AI models to verify the information and understand the context better.
Step 10:Technical Optimization for AI Search Engines
As the first step is important to check if your site is crawlable for AI. Some hosting platforms are blocking AI crawlers by default. You can use tools like, for example, AI Bot Access Analyzer and check if this is the case on your site.
AI search engines need clean, structured technical foundations to understand and cite content effectively. Proper schema markup, mobile optimization, and performance improvements help AI systems crawl and reference your content more reliably.
Using Structured Data and Schema Markup
Structured data provides AI systems with clear context about your content through standardized markup languages. Schema.org markup helps search engines understand whether content contains recipes, articles, reviews, or other specific information types.
AI platforms like Google’s AI Overviews and ChatGPT rely on this structured information to determine content relevance. Pages with proper schema markup appear more frequently in AI-generated responses because the markup removes ambiguity about content meaning.
Essential schema types for AI optimization:
-
- Article schema – Defines publication dates, authors, and article topics
-
- Organization schema – Establishes business credibility and contact information
-
- WebPage schema – Clarifies page purpose and main content areas
-
- BreadcrumbList schema – Shows site hierarchy and navigation structure
Implement schema markup using JSON-LD format in your page’s <head> section. This method loads faster than inline markup and works better with AI crawlers.
Test your structured data using Google Search Console’s Rich Results Test tool or to the Schema Validator tool to ensure proper implementation.
FAQ schema directly matches how people ask questions to AI search engines. This markup format presents question-and-answer pairs that AI systems can easily extract and cite in responses.
Structure FAQ schema with specific questions your audience asks rather than generic topics. AI platforms favor detailed answers with concrete information over vague explanations.
FAQ schema best practices:
-
- Use actual customer or users questions as FAQ headings
-
- Provide complete answers within each FAQ item
-
- Include specific data points and examples
-
- Keep individual answers between 50-150 words
Product schema becomes essential for e-commerce sites targeting AI search visibility. This markup includes pricing, availability, ratings, and detailed product specifications that AI systems reference when answering shopping queries.
Add product schema to individual product pages and category pages. Include aggregate rating data, review counts, and current pricing to increase citation likelihood.
Critical performance factors:
-
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) – Should load within 2.5 seconds
-
- First Input Delay (FID) – Must respond within 100 milliseconds
-
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) – Keep visual stability score below 0.1
Bonus Step: Optimize for Multimodal AI Search
Generative AI is evolving beyond text and increasingly delivers results that blend text, images, and videos. To future-proof your content, don’t stop at written optimization—make sure your visuals are AI-ready too. Add descriptive alt text to images, provide contextual captions, and implement video schema markup so search engines can fully understand your multimedia assets. By aligning your content with multimodal search, you not only improve accessibility but also expand your visibility across the next wave of AI-driven experiences.
Measuring Performance and Maintaining AI Search Visibility
Success in AI search requires tracking specific metrics that show how often content gets cited and maintaining relevance as AI algorithms evolve. Regular monitoring and content updates ensure sustained online visibility across AI platforms.
Tracking AI Mentions and Citations
Monitoring AI mentions requires checking multiple platforms manually or using specialized tools. You can manually test your brand, topic questions on ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews weekly. Or you can use recommended tools like Peec.ai, Ahrefs or SERanking for tracking citations and AI visibility.
Manual tracking methods include:
-
- Searching brand names on major AI platforms
-
- Testing key topic questions monthly
-
- Recording which competitors get cited
-
- Noting citation frequency and position
Manual testing works for small businesses with 5-10 core topics. Larger operations need automated solutions.
Key metrics to track:
-
- Citation frequency – How often content appears as a source
-
- Citation position – Whether content ranks first, second, or third among sources
-
- Topic coverage – Which subjects generate the most mentions
-
- Sentiment analysis – How AI systems describe the brand
Conclusion
Optimizing content for generative AI search engines does not require a big shift in approach. Clear, direct answers help AI systems extract the right information, while schema and structured data improve visibility in AI-generated results. Demonstrating real expertise through author profiles and unique insights builds trust, and linking related content into topical clusters strengthens authority. Finally, remember that AI rewards freshness—regularly updated, relevant content is more likely to be cited. Also, summarise your content by adding Key Takeaways in the beginning- this will help the user and AI to understand what is the main message of your content. Combining clarity, authority, structure, and ongoing updates is the formula for success in the age of AI search.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are there any specific metrics to monitor for content optimized for generative AI search engines?
Yes, for example, brand mention frequency in AI responses indicates visibility success. Citation rates in AI-generated answers reveal content authority.
What are the best practices for content optimization in AI-driven search engines?
Starting content with a summary or key takeaways section is a good technique. This can help AI systems identify the most important information quickly. Adding high authority sources and including quotes or third-party information is also important, as AI algorithms favour content with verifiable data. Language should be simple and without grammatical errors.